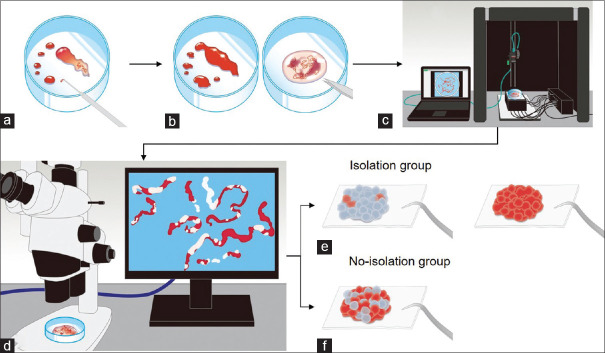
Figure 1.
Study outflow. (a) Step 1: The sample in the puncture needle was initially extruded onto the petri dish by compressing air in the syringe and then using a stylet. (b) Step 2: The earthworm-like core sample obtained was immersed in 10% neutral buffered formalin solution under the stereomicroscope. The liquid component remaining after extruding the sample from the needle was sent for cytologic examination. (c) Step 3: The whitish core sample was sufficiently extended onto a petri dish and soaked in 10% buffered formalin solution, irradiated using nine narrow-band lights, and imaged to obtain multiband image data. (d) Step 4: The SVWCs were measured under the stereomicroscope (×20–40, SZX10; Olympus Medical Systems) using a scale on the microscope monitor screen. (e) Step 5: In the isolation group, the sample in the petri dish was examined, and SVWCs and red components were dissected using injection needles. SVWCs and red components were closely aligned on separate filter papers, immersed in vessels containing 10% neutral buffered formalin, and sent for pathological analyses. (f) Step 6: In the no-isolation group, the samples were closely aligned on filter papers without isolation, immersed in vessels containing 10% neutral buffered formalin, and sent for pathological analyses. AMUS: Automated multiband imaging system; SVWC: Stereomicroscopically visible white core