FIGURE 1.
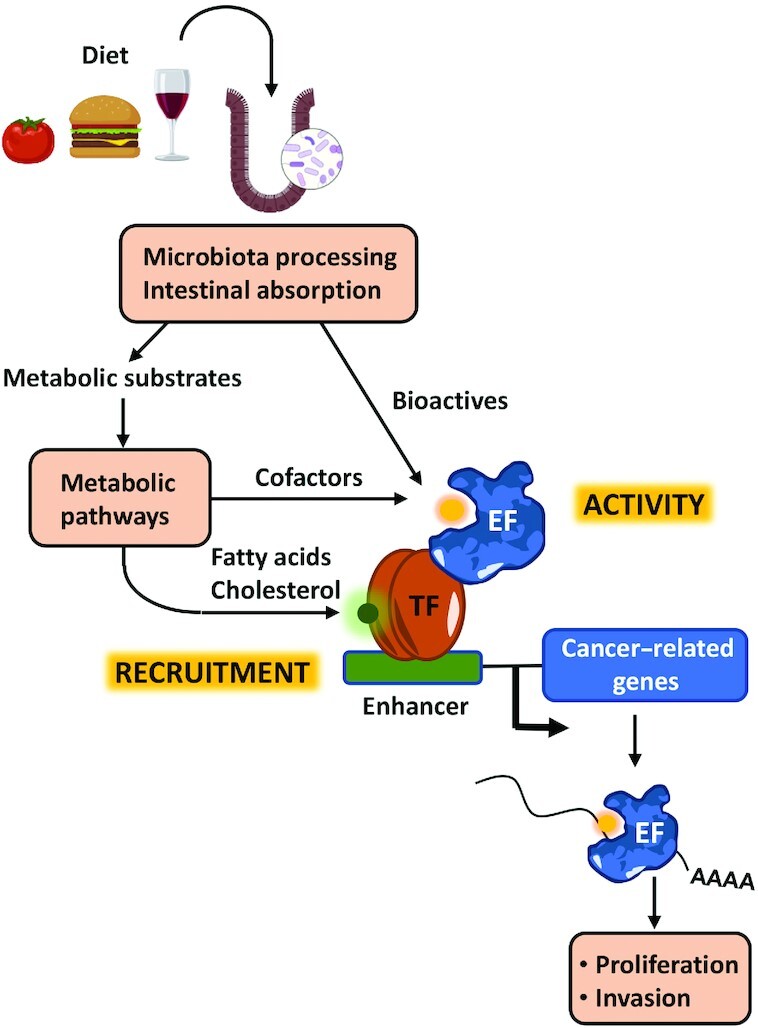
Overview of the topics covered by this review. After intake, food is processed by the microbiota in the intestine and nutrients are absorbed. These might be substrates for metabolic reactions or contain bioactives that can modulate directly the activity of EFs. Metabolic processing can generate cofactors needed for the activity of EFs or products such as cholesterol and fatty acids that modulate the activity of TFs that play a role in the recruitment of EFs to chromatin. EF, epigenetic factor; TF, transcription factor.
