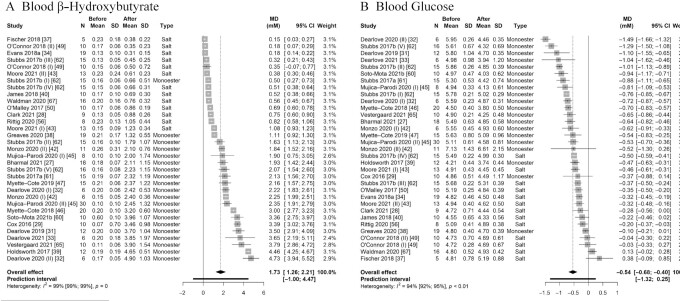
FIGURE 2.
Forest plot of comparisons quantifying the effect of exogenous ketone ingestion on average fasted (A) blood β-hydroxybutyrate and (B) blood glucose in a within-group analysis (i.e., after compared with before consumption of exogenous ketones). Effect sizes (raw MDs, mM) were pooled using a generic inverse-variance pooling method with a random-effects model using the Sidik-Jonkmann τ2 estimator for between-study variance and the Hartung-Knapp adjustment. Significant effects of (A) MD = 1.73 mM (95% CI: 1.26, 2.21 mM; P < 0.001) and (B) MD = –0.54 mM (95% CI: –0.68, –0.40 mM; P < 0.001) were found, indicating that ingestion of exogenous ketones acutely (A) raises blood β-hydroxybutyrate and (B) lowers blood glucose when compared with baseline values. Each square visually represents the weight of the study centered around the study effect size with the corresponding horizontal line showing the study CI. MD, mean difference; monoester, (R)-3-hydroxybutyl (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate ketone monoester.