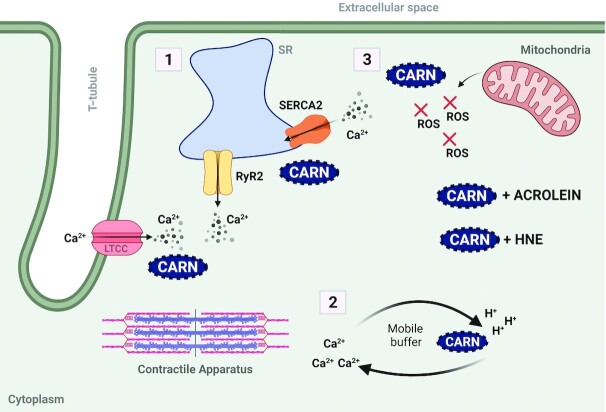
FIGURE 2.
The main physiological roles of carnosine in myocardial function and health: an overview. (1) Carnosine (CARN) regulates EC coupling by influencing calcium (Ca2+) release from the SR via the RyR2 and Ca2+reuptake via SERCA2. (2) Carnosine acts as a mobile Ca2+/H+ buffer, transporting Ca2+ across the cytosol in an H+-coupled manner. (3) Carnosine prevents excessive accumulation of oxidative stress products (e.g., ROS) and acts as a scavenger to form covalent adducts with reactive aldehydes (e.g., acrolein and HNE) (created using BioRender.com). EC, excitation-contraction; HNE, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal; LTCC, L-type calcium channel; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RyR2, ryanodine receptor; SERCA2, sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase; SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum.