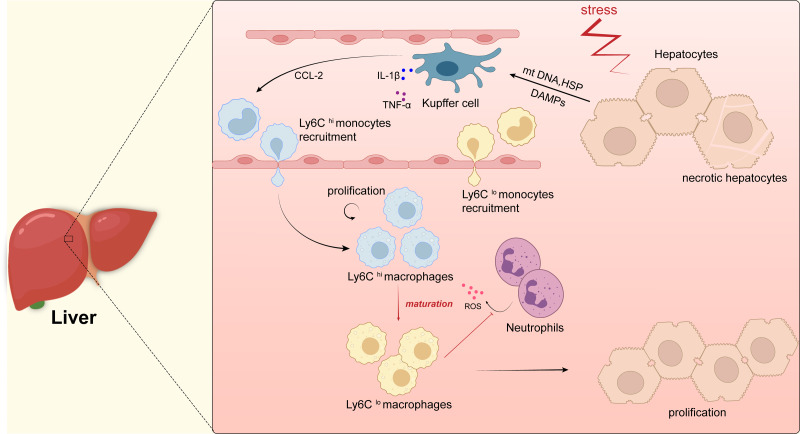
Figure 2. Macrophages in liver.
Kupffer cells are immobilized within the lumen of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) and when hepatocytes are damaged, intracellular components, such as mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) or heat shock proteins (HSP), are released as dangerously relevant molecular patterns (DAMP). DAMPs activate Kupffer cells, which in turn secrete inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF- α, IL-1 β, etc.) as well as CCL-2. CCL-2 recruits Ly6Chi monocytes from the blood to infiltrate tissues and differentiate into pro-inflammatory macrophages (Ly6Chi), which will mature into Ly6Clo macrophages with restorative and anti-inflammatory properties when inflammation resolves, they promote the regeneration of liver parenchymal cells and thus the repair of the liver. In addition, Ly6Clo macrophages inhibit the secretion of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by neutrophils.