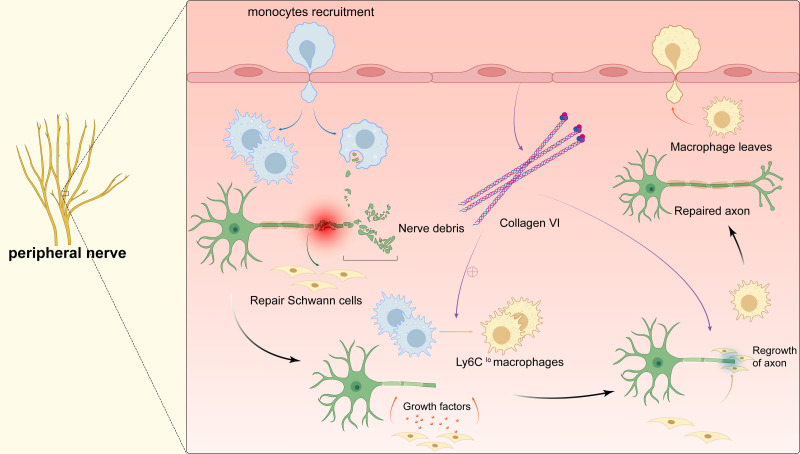
Figure 4. Macrophages in peripheral nerve.
After peripheral nerve injury, monocytes are recruited to the site of injury and differentiate into pro-inflammatory macrophages, macrophages phagocytose myelin debris, and Schwann cells isolate and dedifferentiate into repairing Schwann cells, which secrete cytokines to promote axonal regeneration while the pro-inflammatory macrophages mature into repairing macrophages (Ly6Clo). The polarization of macrophages stimulates the secretion of collagen VI from the membranes of the peripheral nerve, which induces macrophage polarization by positive feedback and participates in axonal repair. The repairing Schwann cells guide axonal regeneration and the repairing macrophages release anti-inflammatory cytokines. After complete nerve regeneration, the macrophages withdraw from the peripheral nerve tissue.