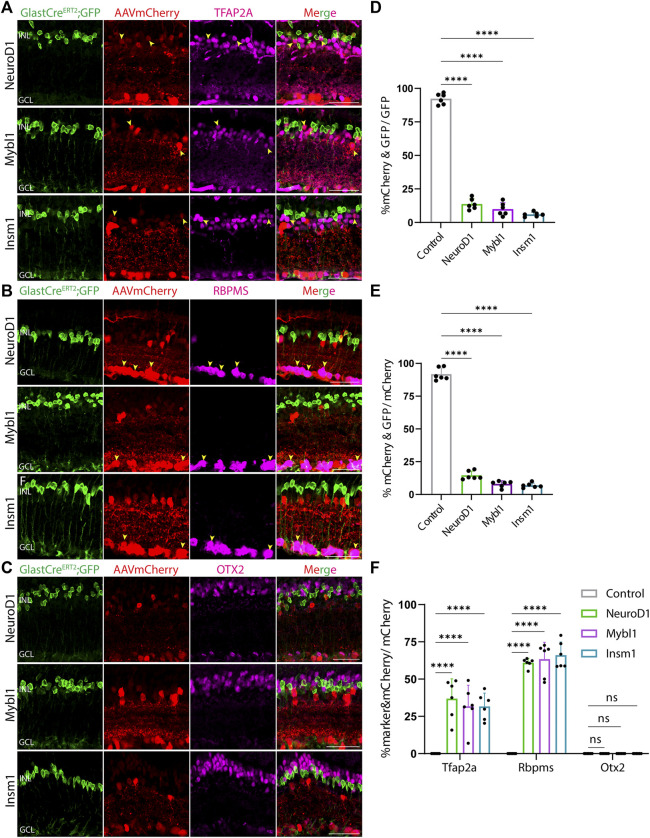
FIGURE 3.
GFAP promoter constructs expressing NeuroD1, Mybl1 and Insm1 show ectopic mCherry expression in amacrine and ganglion cells. Representative immunostaining for GFP, mCherry and 3 neuronal markers: (A) Tfap2a, (B) Rbpms, and (C) Otx2 expression in the retinas collected 21 days post GFAP AAV infection. GFAP-NeuroD1-mCherry, GFAP-Mybl1-mCherry and GFAP-Insm1-mCherry showed little to no colocalization of construct-derived mCherry and Müller glia-specific Sun1-GFP. High levels of mCherry expression in amacrine and ganglion cells, but not in bipolar cells were observed in retinas infected with these GFAP AAV constructs. Yellow arrowheads indicate co-labeled mCherry+ & marker + cells. Quantification of transduction efficiency (mCherry+ & GFP + cells/GFP + cells) (D) and transduction specificity (mCherry+ & GFP + cells/mCherry + cells) (E). Quantification of mean percentage ±SD of marker & mCherry+/GFP cells: Tfap2a+ & mCherry+/GFP + cells (in INL and GCL), Rbpms+ & mCherry+/GFP + cells (in GCL) and Otx2+&mCherry+/GFP + cells (in INL) (F). Significance was determined via one-way ANOVA or two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test: ****p < 0.0001. Each data point in the bar graphs was calculated from an individual retina (n = 6). INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. Scale bar = 40 μm.