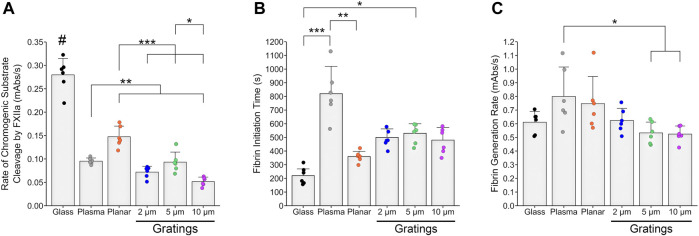
FIGURE 2.
In vitro thrombogenicity of micropatterned PVA. Thrombogenicity of PVA samples was determined by FXIIa activity, fibrin initiation time, and fibrin generation rate using static in vitro assays compared to glass and plasma as positive and negative controls, respectively. (A) FXIIa activity measured by the rate of chromogenic substrate cleavage was significantly reduced for micropatterned PVA compared to planar PVA. FXIIa activity was significantly reduced for the 10 µm gratings compared to the 5 µm gratings. All groups had significantly reduced rate of chromogenic substrate cleavage by FXIIa compared to glass. Plasma was significantly different compared to planar PVA and 10 µm gratings. (B) No significant differences for the initiation time to fibrin formation were observed between planar PVA and micropatterned PVA gratings. We did observe a significantly prolonged initiation time to fibrin formation for 5 µm gratings compared to glass. Plasma had a significant increase in initiation time compared to planar PVA and glass due to adsorption of coagulation proteins to the PVA surface. (C) No significant differences between the rate of fibrin generation were found between PVA groups or glass. Plasma was observed to have a significantly increased rate of fibrin generation compared to the 5 and 10 µm gratings. Sample size correspond to n = 6 for each experiment. *, **, and *** indicate statistical significance (p < 0.05, 0.01, 0.001, respectively). # indicates statistical significance (p < 0.0001) compared to all other experimental groups.