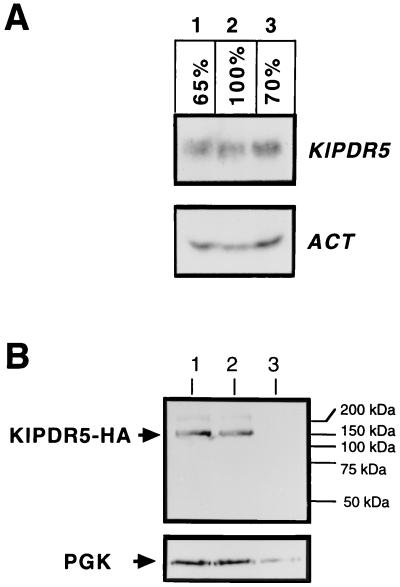
FIG. 6.
Northern and Western blot analysis showing the mRNA abundance of KlPDR5 and the steady-state level of KlPdr5p. (A) Northern blot analysis. K. lactis strains PM6-7A (wild-type, lane 2) and CK254/1 (sit4Δ::URA3, lane 3) were grown in liquid GYP. The KlSIT4-overexpressing strain (lane 1) was PM6-7A transformed with pCXJ3-KlSIT4 (9) and grown in GYP supplemented with G418 at 200 μg/ml to maintain the plasmid. Total RNAs extracted from the strains were electrophoresed on a 1.2% agarose-formaldehyde gels, transferred to nylon membranes, and hybridized at high stringency with the 32P-labeled KlPDR5 and actin probes. The relative abundance of the KlPDR5 mRNA was estimated by PhosphorImager analysis by using the ACT1 mRNA as an internal control for sample loading. (B) Western blot analysis. Protein extracts were prepared from PM6-7A (wild-type, lane 2) and CK432/8 (sit4, lane 1) transformants carrying pCXJ18-KlPDR5HA and separated on a 4-to-20% gradient SDS-polyacrylamide gel before being blotted onto a nylon Immobilon-P membrane (Millipore) and probed with a monoclonal anti-HA antibody. A parallel membrane was probed with the anti-3-phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) antibody to demonstrate the amounts of proteins loaded on each lane. Cell extracts from untransformed PM6-7A were included as a negative control for the lack of nonspecific cross-reactions of the antibodies with K. lactis proteins.