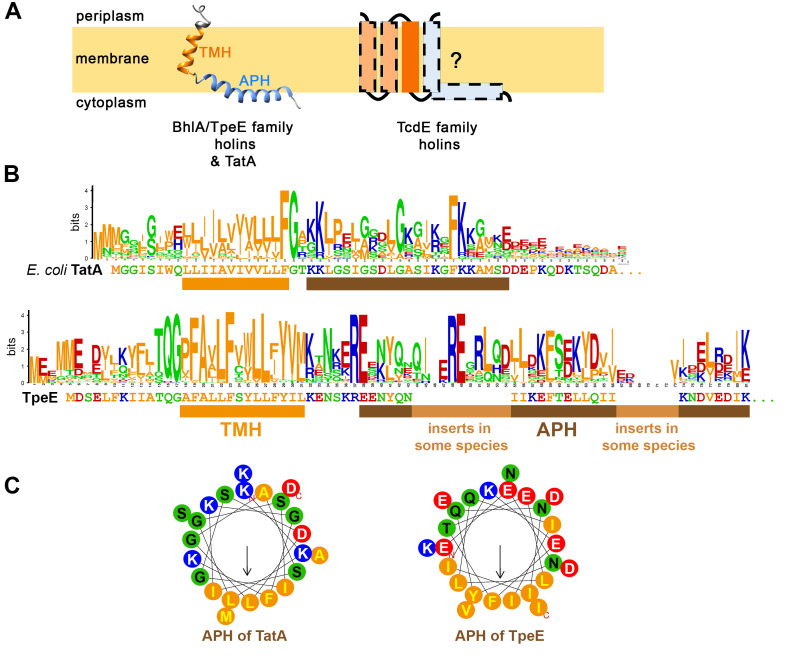
Figure 4. FIGURE 4: Structural comparisons of holins and TatA.
(A) Schematic topology or BhlA/TpeE family holins and TatA in comparison to predicted topologies of TcdE. Note that TcdE homologs have always one TMH in common but can have up to three more predicted TMHs, resulting in a largely unclear topology. (B) WebLogo analysis of TatA and TpeE sequences [101], indicating conserved regions and the general characteristics of the residues (hydrophobic, orange; hydrophilic but uncharged, green; positively charged, blue; negatively charged, red). The corresponding sequences of E. coli TatA and C. perfringens TpeE are shown underneath the WebLogo diagram. The short consecutive hydrophobic region of the TMH is underlined in orange, the amphipathic helix (APH) is underlined in brown. The sequence alignment for the WebLogo-analysis has been made by Clustal-Omega [102] with 40 TatA sequences from very diverse organisms (α- β -, γ - δ -, and ε -Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Cyanobacteria, Chloroflexaceae, Thermodesulfobacteria, and Aquificae), and with 100 TpeE homologs (TpeE homologs are only found in Firmicutes). (C) Comparison of the APHs of E. coli TatA and C. perfringens TpeE by helical wheel views. TMH predictions were done by TMHMM2 [46], and helical wheel views and APH visualizations were done using HELIQUEST [103].