Fig. 2.
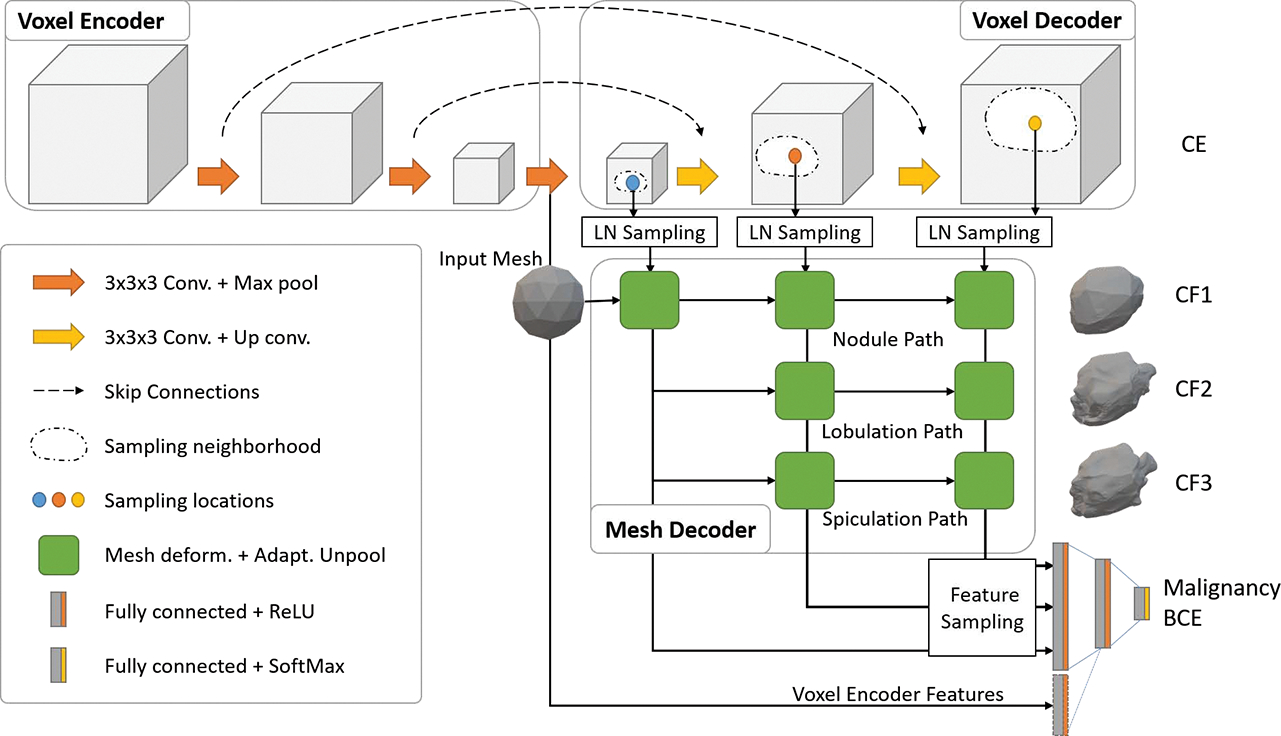
Depiction of end-to-end deep learning architecture based on multi-class Voxel2Mesh extension. The standard UNet based voxel encoder/decoder (top) extracts features from the input CT volumes while the mesh decoder deforms an initial spherical mesh into increasing finer resolution meshes matching the target shape. The mesh deformation utilizes feature vectors sampled from the voxel decoder through the Learned Neighborhood (LN) Sampling technique and also performs adaptive unpooling with increased vertex counts in high curvature areas. We extend the architecture by introducing extra mesh decoder layers for spiculation and lobulation classification. We also sample vertices (shape features) from the final mesh unpooling layer as input to Fully Connected malignancy prediction network. We optionally add deep voxel-features from the last voxel encoder layer to the malignancy prediction network.
