Fig. 4.
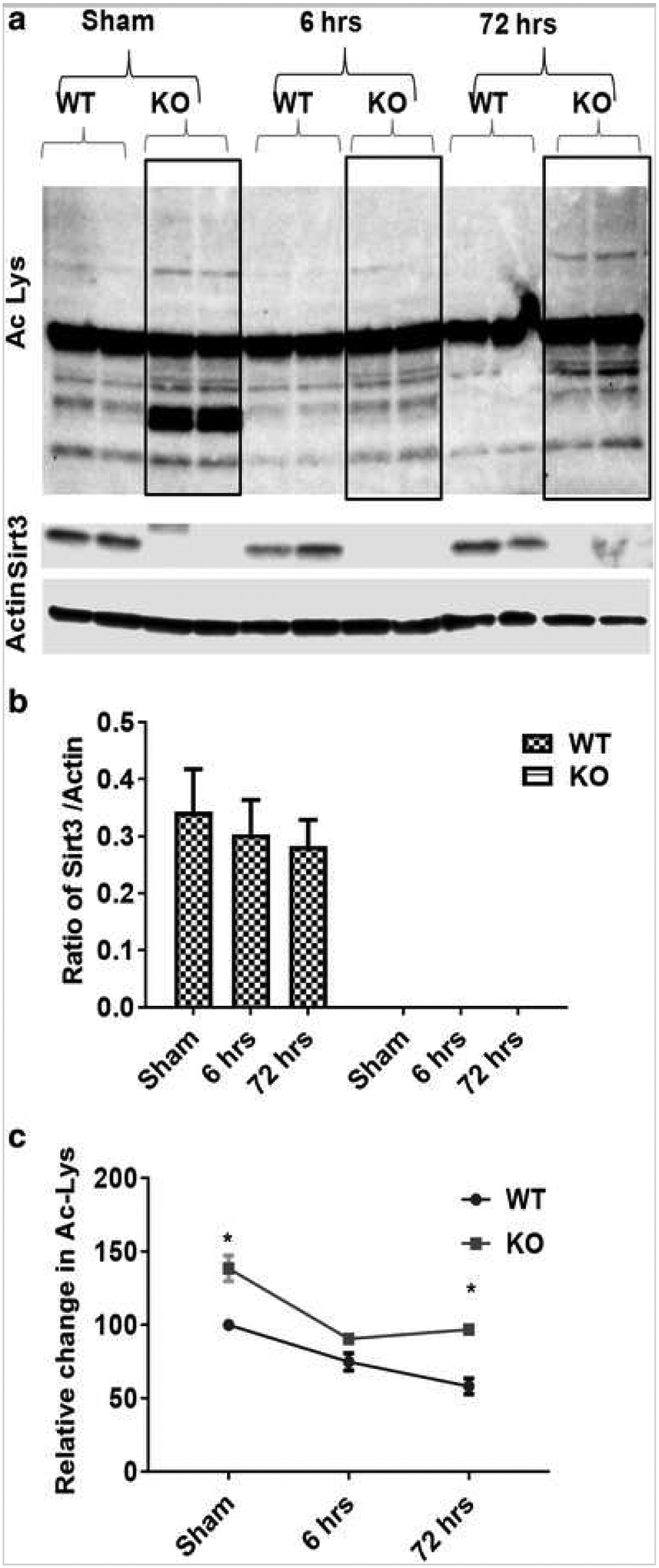
Sirt3 regulates protein acetylation after stroke. a Western blot images for Sirt3 and Ac-lysine expression using whole cell lysate from Sirt3 KO and WT mice after stroke. b Temporal analysis of Sirt3 protein expression after sham, 60 min/6 h or 60 min/72 h (3 days) after stroke showed no change in total Sirt3 protein levels. c However, temporal analysis of Ac-lys indicates two important findings; first, the level of Ac-lysine protein was higher (*p < 0.05 vs. WT, Student’s t test) in KO compared to their respective time point Controls, and second, the amount of Ac-lysine decreases progressively after stroke (*p < 0.05 a one-way ANOVA). A two-way ANOVA found a significant interaction between stroke surgery and genotype [F (2,10) = 31.39 p < 0.001] as well as the main effect of both stroke [F (2,10) = 206 p < 0.001] and genotype [F (1,5) = 246.9 p < 0.001] on Ac-lys expression (n = 4mice/group/time point; graphs show mean + S.E.M.).
