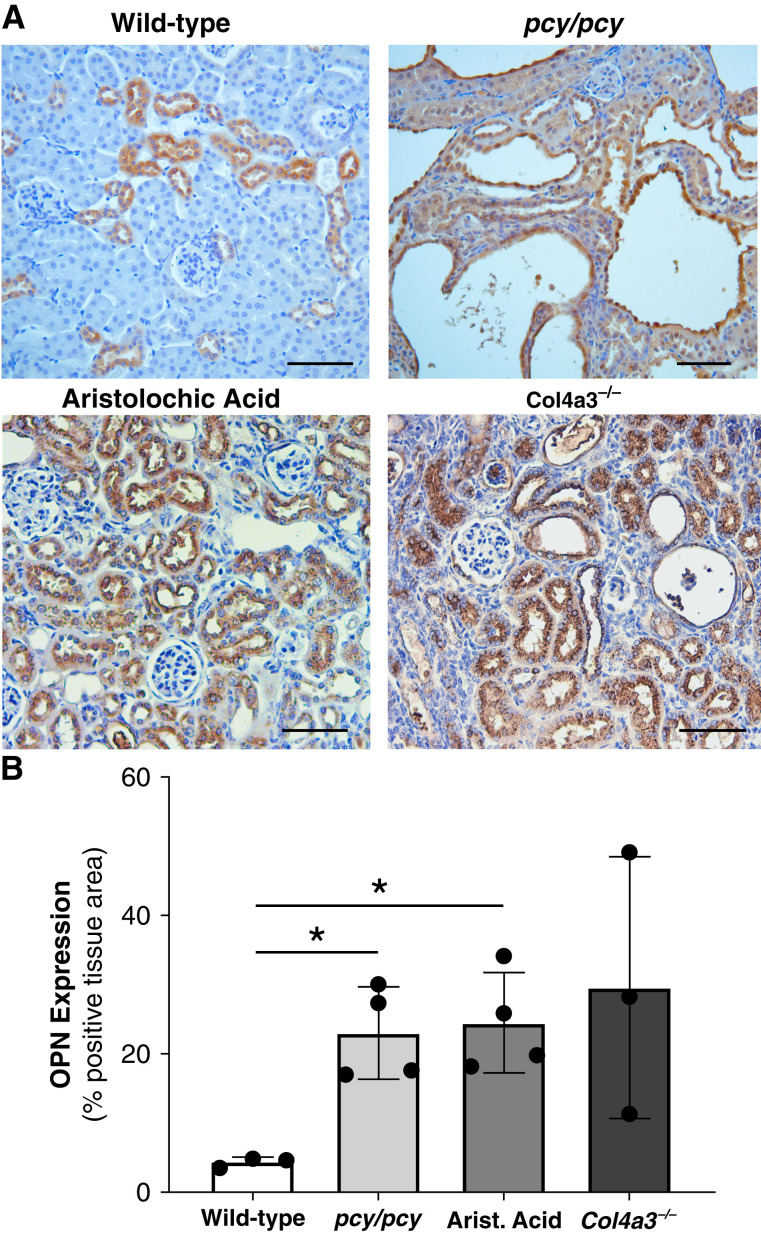
Figure 1.
Kidney osteopontin (OPN) expression is increased in various CKD murine models. (A) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) of OPN protein expression (brown) in kidneys from mice with normal kidney function (wild type [WT]), cystic kidney disease (pcy/pcy), chronic tubular injury/fibrosis (aristolochic acid), and primary glomerulonephritis (Alport disease; Col4a3−/−). WT mice exhibit OPN staining in distal tubules, whereas all other CKD models demonstrate diffuse OPN staining in all nephron segments. (B) Quantification of OPN IHC staining confirmed the higher OPN expression in CKD models. Representative images were selected from a minimum of three per group; scale bar=100 µm for all images (*P<0.05 versus WT by t test with Welch’s correction; data presented as mean±SD).