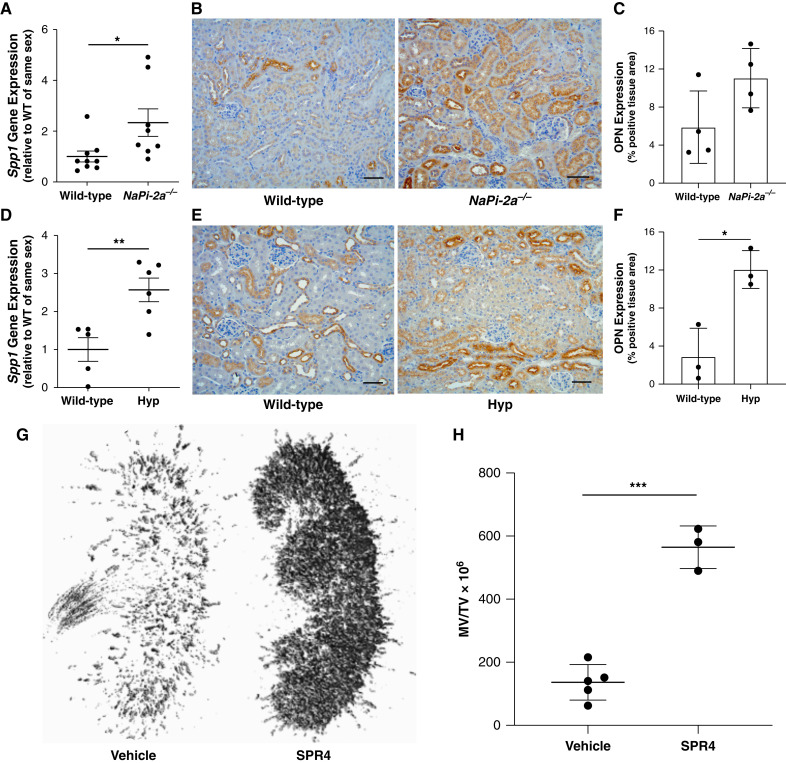
Figure 5.
Kidney OPN and its ASARM peptide sequence serve a critical function in preventing nephrocalcinosis in the setting of phosphaturia. Two separate phosphaturic murine models, Napi2a−/− and Hyp mice, exhibit increased kidney OPN expression. (A) NaPi-2a−/− mice demonstrate increased kidney Spp1 (OPN) gene expression compared with WT littermates as assessed by quantitative real-time PCR. Moreover, (B) IHC staining revealed increased tubular OPN protein expression (brown) in kidney sections from NaPi-2a−/− mice. (C) Quantification of total OPN expression from images of mid-kidney sagittal cross-sections stained by IHC validated these observations. Similarly, phosphaturic Hyp mice exhibited (D) increased kidney Spp1 (OPN) gene expression, and (E) and (F) increased expression of OPN protein by IHC staining (all histology scale bars=50 μm). (G) Neutralization of the mineral binding (ASARM) peptide sequence of OPN with SPR4 peptide in Hyp mice results in severe nephrocalcinosis, as demonstrated by representative μCT images of whole kidneys from Hyp mice treated with either vehicle or SPR4. (H) Quantification of kidney mineralized tissue volume relative to total kidney volume (MV/TV) for all Hyp mice treated with either vehicle or SPR4 (for all analyses, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 by Student’s t test; n≥3 per group; data presented as mean±SD).