Fig. 5. Dual IGF1R and FAK inhibition affects viability and signaling in EGFR-mutant NSCLC cells.
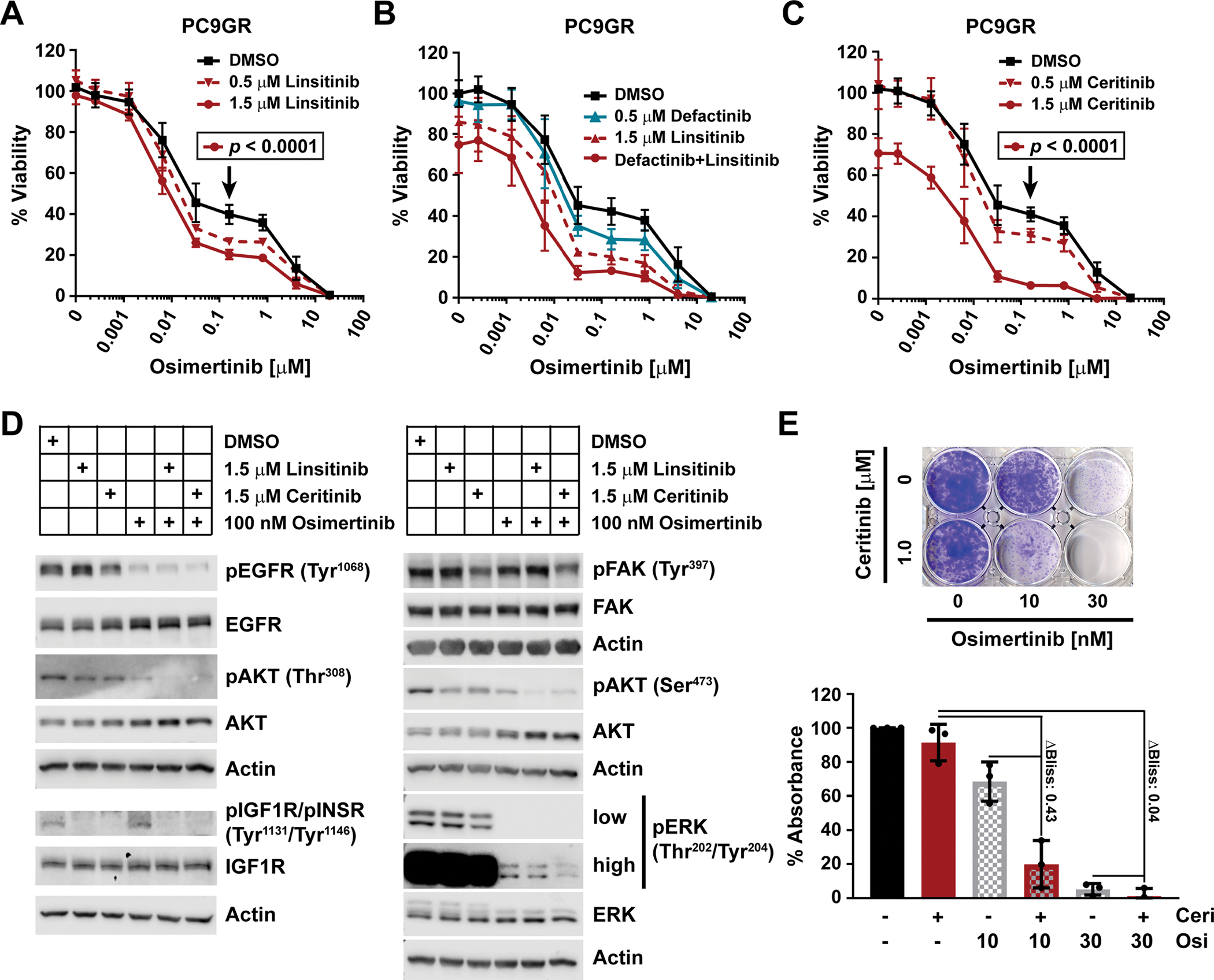
(A to C) Viability as determined by CTG of PC9GR cells plated in RPMI10 and treated after 24 hours with osimertinib in combination with stated concentrations of linsitinib (A; n=3 experiments), defactinib, linsitinib, or both (B; n=2), or ceritinib (C; n=3) for 72 hours. 100% viability was set to total luminescence in DMSO-only treated cells. Each experiment (n) was performed as technical triplicates, which were averaged before determining the mean ± SD and significance across biological replicates, by unpaired t test with single pooled variance and Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparison test for (A) and (C). Black arrows mark the specific concentration of the respective control curve (in black) compared in each experiment. (D) Western blot analysis of the phosphorylated and total fractions of the indicated proteins at 30 min after drug application. PC9GR cells were plated in RPMI10 and the media was changed the next day to RPMI10 containing DMSO, linsitinib, ceritinib, osimertinib, or combinations thereof as indicated. Actin, loading control. Blots are representative of at least three biological replicates. Quantifications are in fig. S6, and LI-COR scans in fig. S11. (E) Representative clonogenic viability assay for PC9GR cells (1500 cells/well) treated with osimertinib and/or ceritinib at the indicated concentrations at day 1 and incubated for 10 days. Data are quantification of extracted crystal violet absorbance, mean ± SD of three biological replicates.
