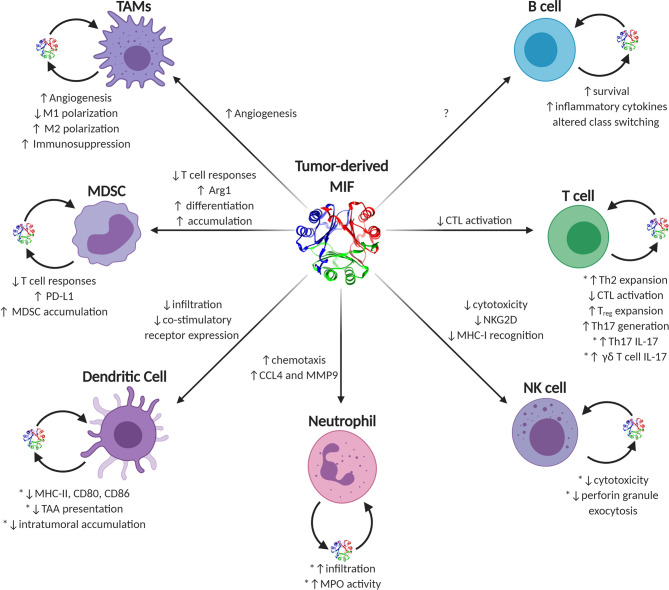
Figure 3.
Known and putative effects of MIF on tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Graphical depiction of immune effector cells known to be influenced by MIF. Sources of intratumoral MIF include both paracrine acting tumor-secreted and autocrine acting immune cell-secreted MIF. Phenotypes ascribed to tumor-derived MIF on individual cell types are listed next to each corresponding arrow to each cell type, while autocrine-associated activities are noted next to each cell with the caveat that those activities validated using recombinant MIF sources are noted with an asterisk. CCL4, inflammatory chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 4; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; MMP9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; MPO, myeloperoxidase; NK, natural killer; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; TAA, tumor-associated antigens; TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; Th, T helper. Figure has been reprinted from Noe JT, Mitchell RA. MIF-dependent control of tumor immunity. Front Immunol 2020;11:609948.10