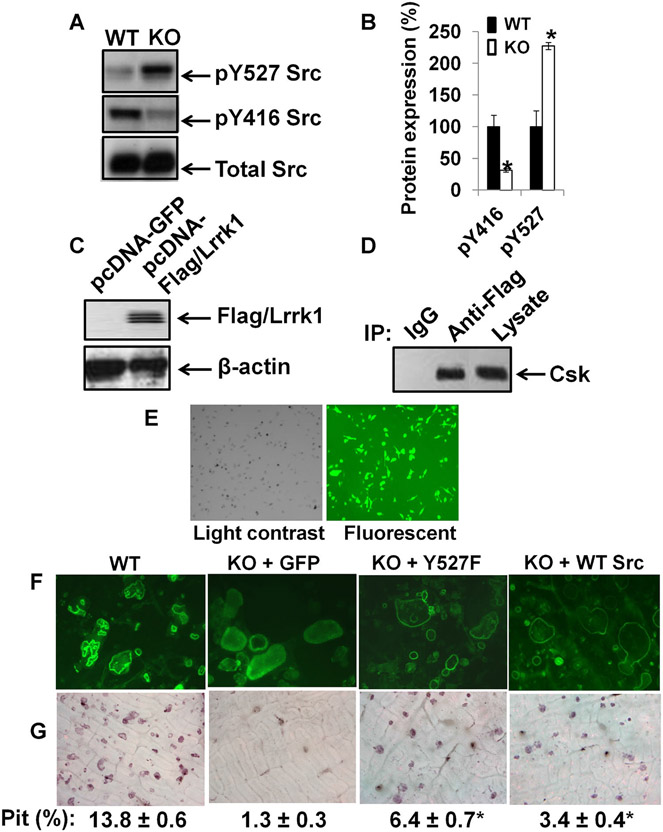
Fig. 9.
Lrrk1 interacts with Csk, and is involved in the regulation of c-Src phosphorylation. (A) Increased pY527 c-Src and decreased pY416 c-Src in Lrrk1 KO osteoclasts. A representative image of a Western blot is shown. (B) Quantitative data from Western blots from three independent experiments with three replicates each time. (C) Overexpression of human Lrrk1 (hLrrk1) and Flag fusion protein in RAW264.7 cells. (D) Interaction of hLrrk1 with Csk in transiently transfected RAW264.7 cells, detected by immunoprecipitation. (E) High efficiency of MLV-mediated transduction in Lrrk1-deficient osteoclast precursors, as measured using a GFP reporter. (F) F-actin ring formation in osteoclasts expressing GFP and Y527F Src, respectively. (G) Overexpression of constitutively active c-Src in Lrrk1-deficient osteoclasts rescues bone resorptive function. Primary osteoclast precursors derived from spleens of Lrrk1 KO mice were transduced with MLV-GFP, MLV-Y527F, or MLV-WT Src. Cells were differentiated on bone slices for pit formation assays.