FIGURE. 5.
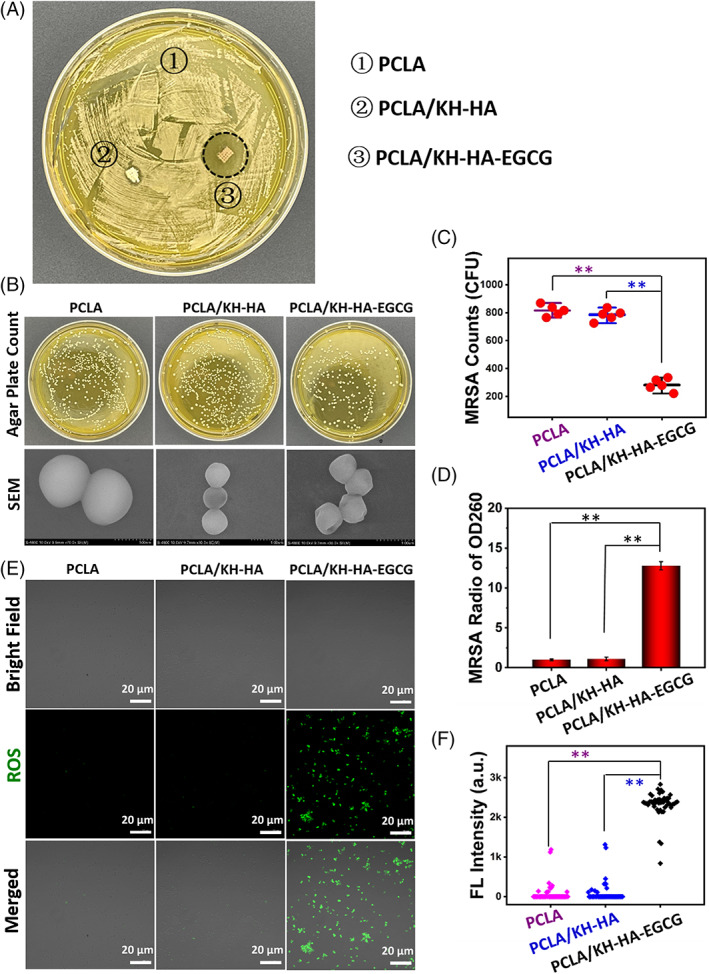
Antimicrobial activity of the coated scaffolds. (A) The zone of inhibition (ZOI) study of different PCLA scaffolds for MRSA. (B) The intuitive agar plate counts and SEM images of structural integrity of the treated MRSA in different groups. (C) Agar plate count statistics of MRSA corresponds to B. (D) The content of nucleic acids in MRSA culture medium quantified after treatment with different PCLA scaffolds. (E) Fluorescence staining shows the burst of ROS in MRSA after treatment with different PCLA scaffolds. (F) Fluorescence intensity analysis corresponds to E. Each point represents the fluorescence intensity of an individual MRSA cell. Data are presented as the mean ± SD, **p < 0.01. MRSA, methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus; PCLA, polymerization of caprolactone and lactide; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SEM, scanning electron microscopy
