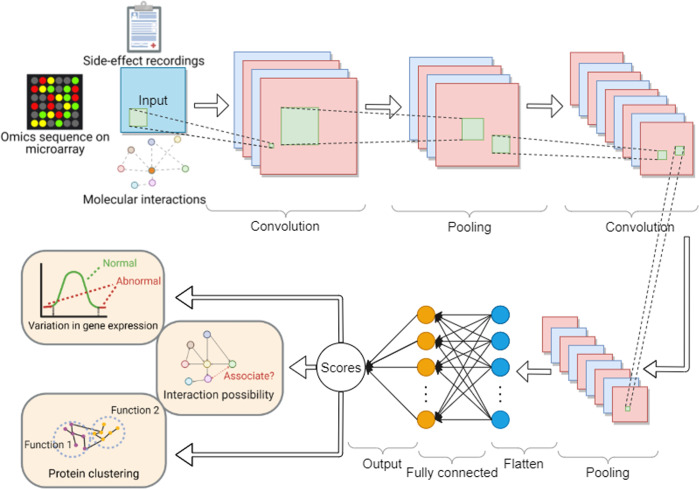
Fig. 5. A convolutional neural network.
This neural network is comprised of an input layer, convolutional layers (that extract features from hyperplanes of input data by projection/convolution), pooling layers (that reduce the spatial size and mitigate the locational sensitivity), flatten layer (that flattens the features and feeds them into the artificial neural network), fully connected layer (that learns nonlinear function of the extracted features) and an output layer. The input is the raw features such as molecules sequence patterns, gene regulation annotations and patterns, molecular interaction network motifs, molecular structures and structural associations, drug chemical structures, drug side-effect reports, and so on. The output can be the predicted classification (e.g., molecular binding profiles) and regression (e.g., quantified molecular binding affinities) when obtaining new samples.