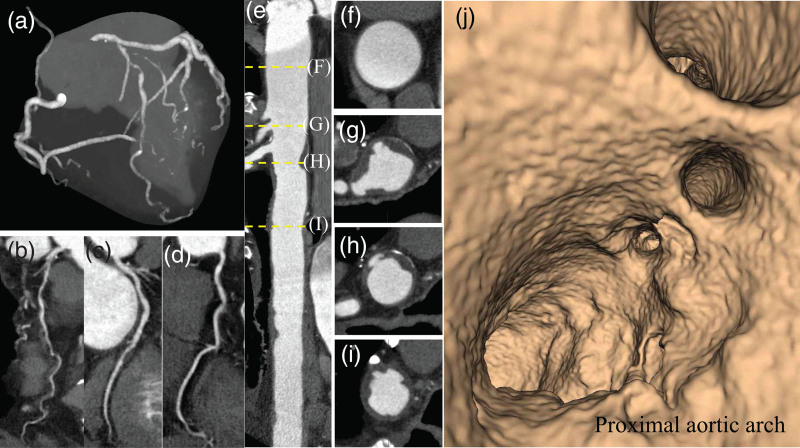
Fig. 2.
Computed tomography coronary angiography with wide-volume scanning images to visualize the thoracic aorta together with the coronary arteries in an obstructive CAD patient without stroke history. (a) Maximum intensity projection image of coronary arteries with multivessel obstructive CAD. Curved planner reconstruction images of LAD (b), LCX (c), and RCA (d). (e) Straight CPR image of contrast-enhanced CT angiography for the thoracic aorta. The ascending aorta (f) and ulcered AAPs ≥ 4 mm (g and h). (i) The descending aortic plaque with ulceration. (j) Fly through view of the aortic arch from proximal to distal aortic arch. Irregular luminal surface indicates complex AAPs partially corresponding to (g and h). AAPs, aortic arch plaques; CAD, coronary artery disease; CPR, curved planar reformation; LAD, left anterior descending coronary artery; LCX, left circumflex coronary artery; and RCA, right coronary artery.