Figure 1: Schematic of skin aging and senotherapeutic treatment.
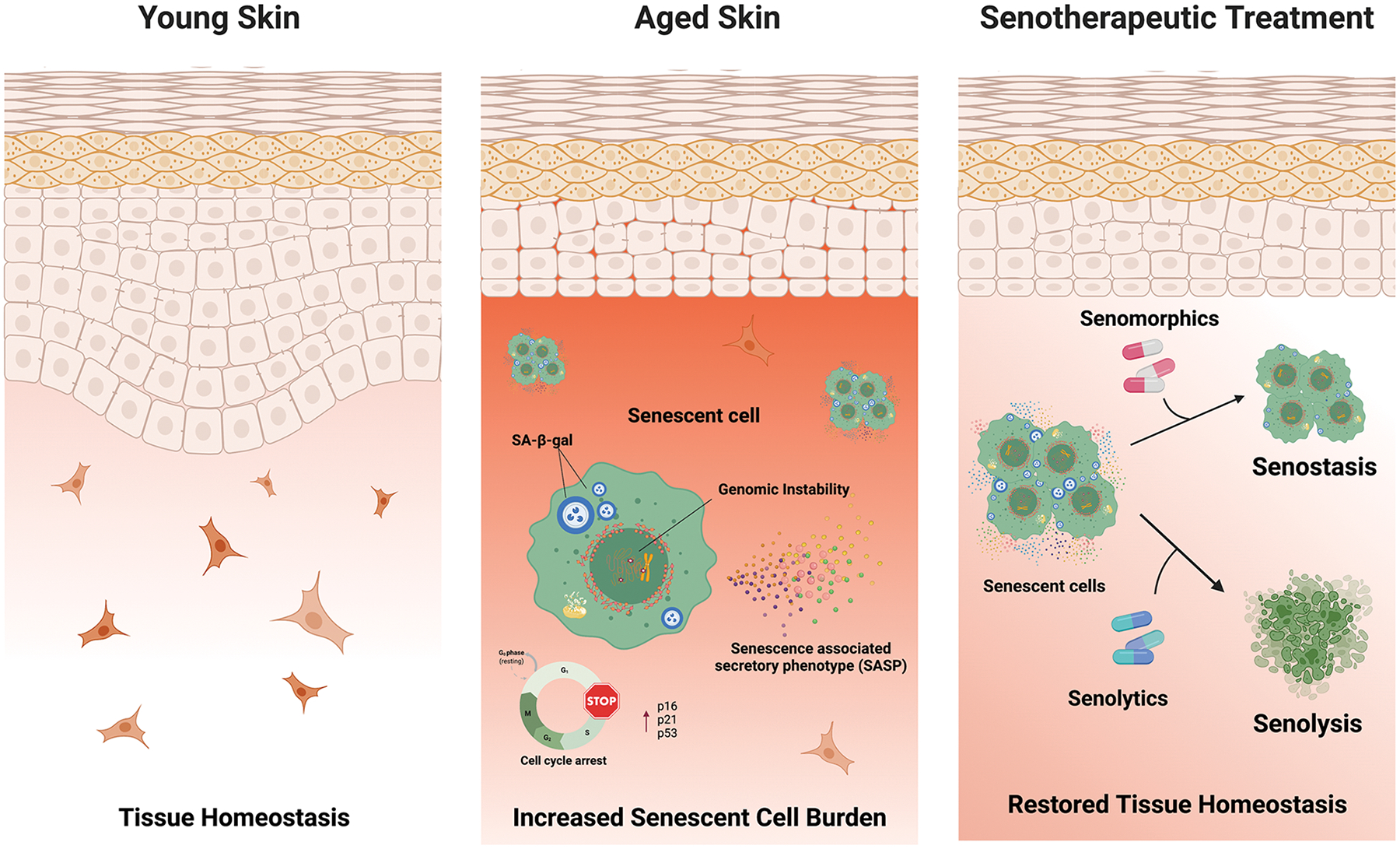
Skin aging is associated with many phenotypic alterations including increased permeability and stiffness of the stratum corneum, flattening and loss of rete ridges in the epidermal-derma junction, alterations in cellular composition, increased senescence cell burden and other aging phenotypes that reduces the protective function and wound healing of the skin. However, senotherapeutic treatments that selectively target senescent cells promoting their clearance (senolysis) or suppression of their SASP (senostasis) decreases inflammation, attenuates tissue dysfunction, and improves regenerative capacity in skin.
