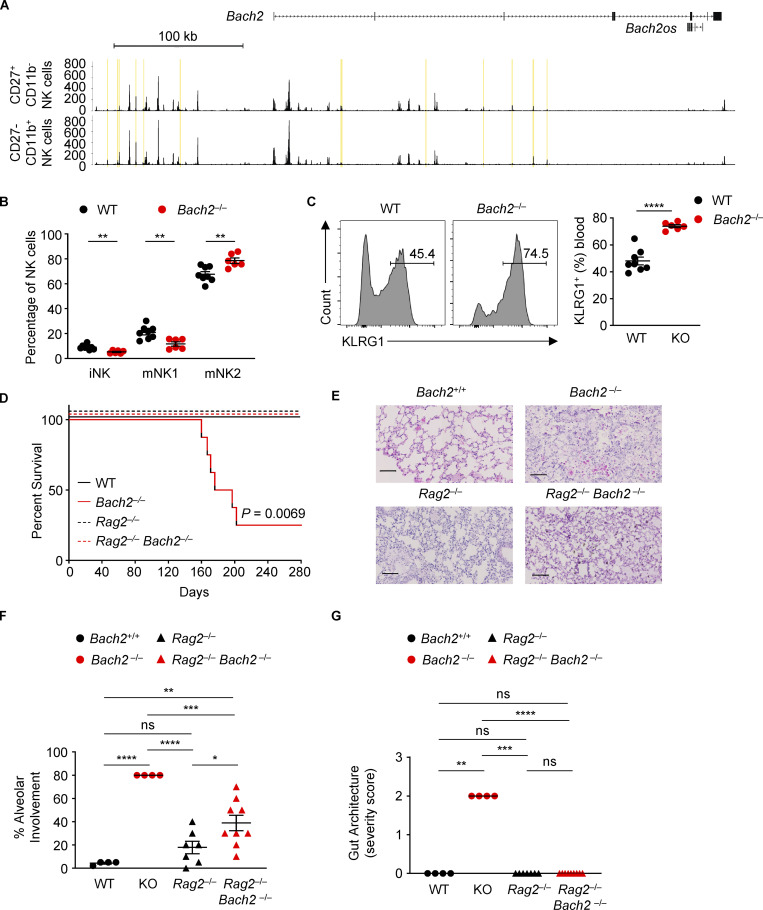
Figure S1.
Bach2 deficiency in innate lymphocytes is not associated with a lethal inflammatory phenotype. (A) Genomic tracks depict histograms of normalized reads (y axis) plotted by genome position (x axis) near and within the Bach2 locus for BM-derived CD27+ CD11b− and CD27− CD11b+ NK cells (GSE109517; Zook et al., 2018). Yellow boxes highlight differentially accessible peak regions. (B) Percentages of NK cells of indicated phenotypes within NK cells from blood samples of WT and Bach2−/− mice. (C) Representative histograms (left) and replicate measurements (right) of KLRG1 expression on NK cells in blood samples from mice of indicated genotypes. Numbers in gates indicate percentages. (D) Kaplan-Meier plot showing survival of WT, Bach2−/−, Rag2−/−, and Rag2−/− Bach2−/− animals. Logrank test; P = 0.0069. (E) Representative histological images of lungs taken from aged animals of indicated genotypes. Scale bar = 100 µm. (F) Replicate measurements of percentage alveolar involvement of lungs, as shown in E. (G) Histopathology scoring of gut samples taken from aged animals of indicated genotypes. ns, not significant (P > 0.05); *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001. Data representative of two independent experiments with six to eight mice per group (B–F). Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test (B and C). Ordinary one-way ANOVA (F). Kruskal–Wallis test (G). Bars and error are mean and SEM.