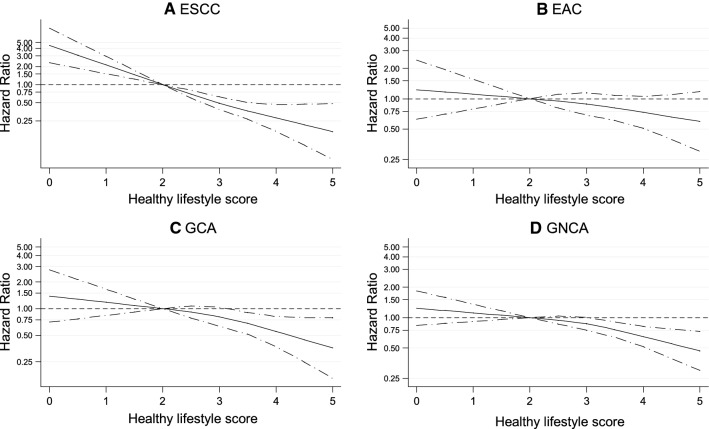
Fig. 1.
Spline regression curves for the association between healthy lifestyle score (HLS) and risk of A esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, B esophageal adenocarcinoma, C gastric cardia adenocarcinoma, and D gastric non-cardia adenocarcinoma, Netherlands Cohort Study (NLCS). Solid lines represents point estimates and dashed lines represent 95% confidence intervals. Multivariable HRs were calculated by restricted cubic spline regression (using 3 knots) adjusting for: age at baseline (years; continuous), sex, cigarette smoking frequency (number of cigarettes per day; continuous, centered) and duration (number of years; continuous, centered), highest level of education (primary school or lower vocational, secondary or medium vocational, and higher vocational or university), family history of esophageal cancer, family history of gastric cancer (respectively), chronic diseases at baseline: myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, stroke, hypertension, diabetes, asthma or bronchitis (no, yes), energy intake (continuous, kcal/day). P-values for non-linearity tests were 0.596 for ESCC, 0.744 for EAC, 0.466 for GCA and 0.268 for GNCA. Abbreviations: ESCC, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; EAC, esophageal adenocarcinoma; GCA, gastric cardia adenocarcinoma; GNCA, gastric non-cardia adenocarcinoma; HLS, healthy lifestyle score