Fig. 1: Schematic representation for generation of osmotic and hydrostatic pressure.
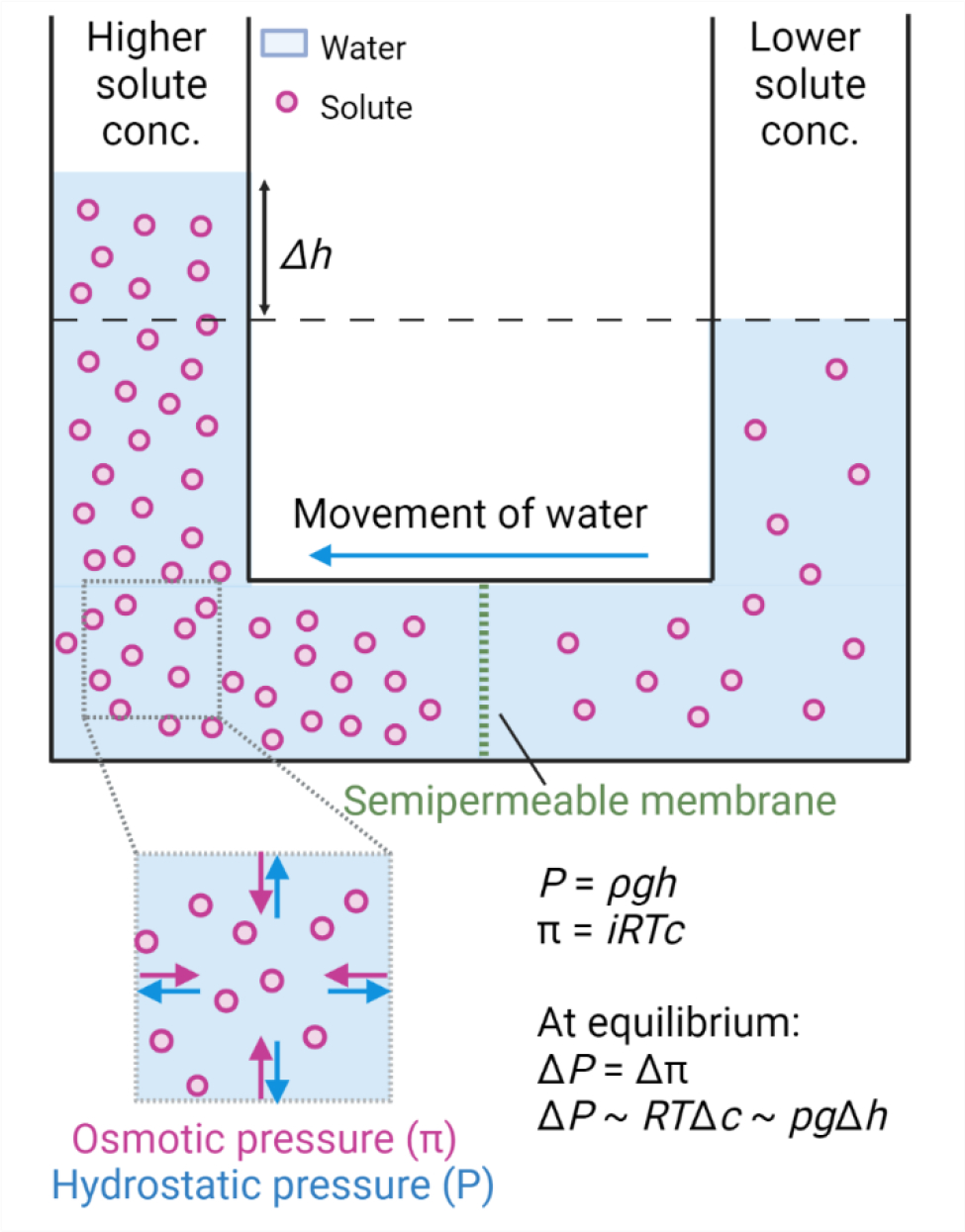
Imbalance in the solute concentration across the semipermeable membrane generates osmotic pressure π leading to the flow of water from lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration. π = iRTc, where i is the van’t Hoff factor, R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature and c is the solute concentration. The counteractive pressure to osmotic pressure is hydrostatic pressure P = ρgh, where ρ is the density of the liquid, g is gravity, and h is the height of the liquid. At chemical equilibrium, osmotic pressure is equal to hydrostatic pressure.
