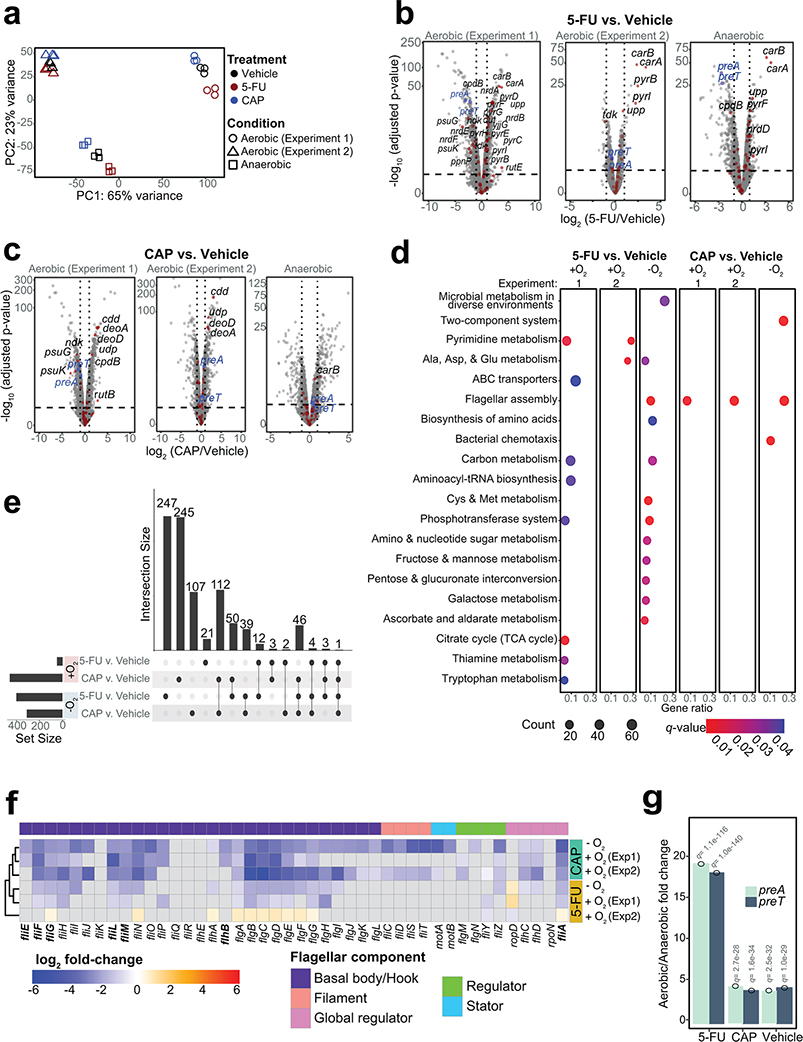
Fig. 2|. Shared and unique transcriptional response to the related fluoropyrimidines 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and capecitabine (CAP) during aerobic and anaerobic growth.
(a) Principal component analysis of E. coli MG1655 transcriptomes under different treatments in aerobic and anaerobic conditions (n=3 biological replicates; 2 independent experiments were conducted for aerobic growth). (b,c) Volcano plots of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) [False Discovery Rate (FDR)<0.1, |log2 fold-change|>1, significance limits are marked with dash lines; Wald test with Benjamini-Hochberg correction]. DEGs involved in pyrimidine metabolism are labeled by gene name and marked with a red dot. preT and preA are labeled in blue. (d) Pathway enrichment analysis following 5-FU and CAP exposure under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database was used to test for pathway enrichment (q-value<0.1, Hypergeometric test with Benjamini-Hochberg correction from enrichKEGG function in clusterProfiler98). (e) Upset plot comparing the fluoropyrimidine responsive DEGs under different growth conditions (Supplementary Table 5). The numbers on top of the vertical bars represent the number of DEGs unique to a single comparison (single dot) or shared among multiple comparisons (connected dots). The set size refers to a total number of DEGs in a single comparison (DEGs defined as FDR<0.1, |log2 fold-change|>1; Wald test with Benjamini-Hochberg correction). (f) Heatmap of transcriptional changes of 44 genes involved in flagellar biosynthesis in response to fluoropyrimidine treatments under anaerobic and anaerobic conditions. Gray boxes indicate non-significant changes (FDR>0.1). Bolded genes indicate DEGs that are down-regulated in 5-FU evolved strains reported in literature36. (g) preT and preA transcript levels are significantly lower during anaerobic growth relative to aerobic growth irrespective of the presence of fluoropyrimidines (q-value<0.1, DESeq).