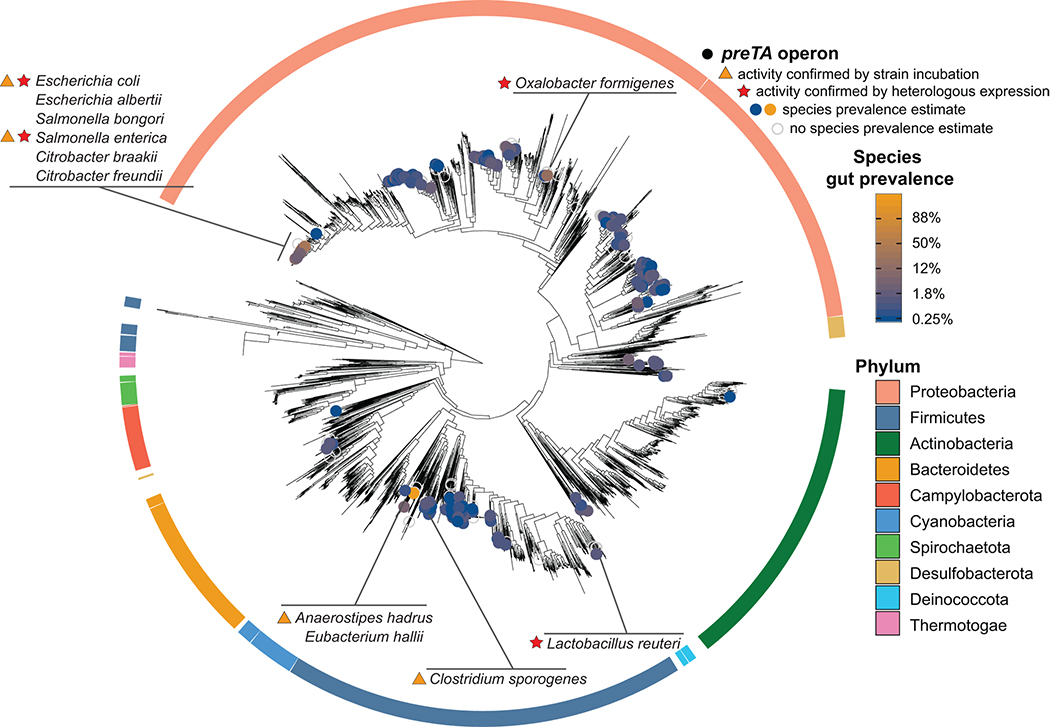
Fig. 5|. Functional orthologs of the preTA operon are widespread in human gut bacterial strains from the Firmicutes and Proteobacteria phyla.
Distribution of bioinformatically-identified preTA operons across RefSeq bacterial isolate genomes. A phylogenetic tree of these genomes made using a concatenated alignment of single-copy marker genes is shown. Bacterial species identified as carriers of putative preTA operons are identified with colored circles, where the color of the circle corresponds to prevalence levels from human gut microbiomes (blue: low prevalence; orange: high prevalence; unfilled grey: no prevalence estimate). Phylum-level annotations are shown as colored ring segments surrounding the tree for the ten phyla with the most species in Refseq. Specific taxa of interest are highlighted in call-out boxes. Red stars indicate preTA operons that have been validated to inactive 5-FU by heterologous expression from E. coli ΔpreTA (see Extended Data Fig. 8a). Orange triangles indicate preTA-positive bacterial species (or close relatives) for which we have confirmed 5-FU inactivation in vitro (see Extended Data Fig. 8b). A list of preTA-positive bacteria can be found in Supplementary Table 8.