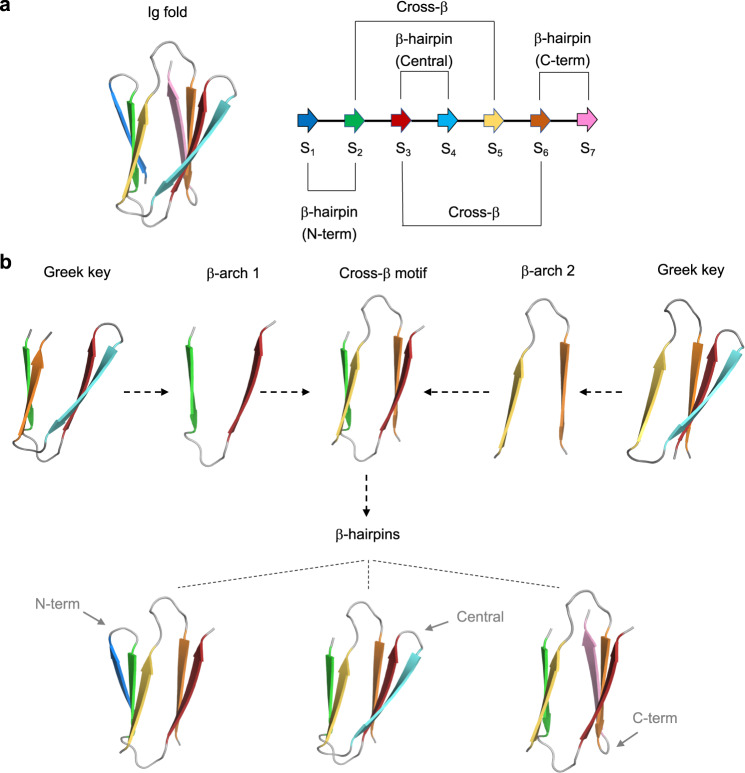
Fig. 1. Topology of immunoglobulin-like domains.
a Three-dimensional cartoon representation of an Ig structure formed by seven β-strands (left); and backbone hydrogen bond patterns (annotated thin lines) between paired β-strands along the sequence (right). Cross-β interactions have higher sequence separation (and higher contact order) than β-hairpins, which slows down folding. b β-arches of the cross-β motif belong to two contiguous and distinct Greek key motifs: with 2 β-strands in each β-sheet (left); and with 3 β-strands in one β-sheet and 1 β-strand in the other (right). From the folding and design perspective, the main limiting factor for correctly assembling the Ig structure is formation of the cross-β motif, since the three β-hairpins can form independently of one another.