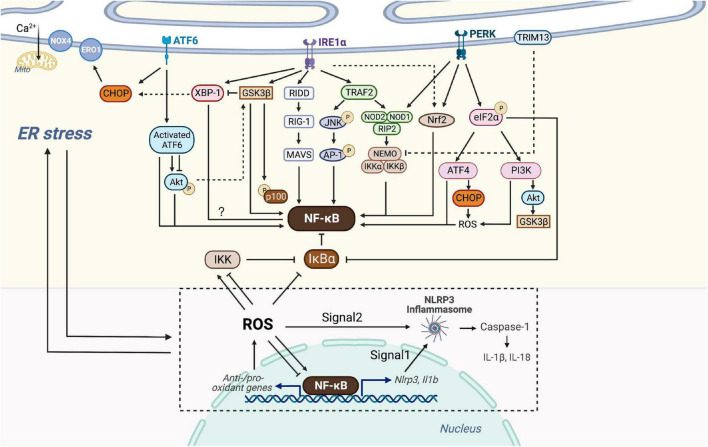
FIGURE 3.
Crosstalk of NF-κB and ER stress. Three branches of UPR (IRE1α, PERK, and ATF6) of ER stress are able to intersect with NF-κB. Activated IRE1α recruits TRAF2, which activates JNK and then AP-1 or associates with IKK probably via NOD1/2 and RIP2. IRE1α is also linked with the RIDD/RIG-I/MAVS pathway and GSK3β to activate NF-κB. IRE1α oligomerization increases XBP-1 expression which might be associated with decreased NF-κB expression, but GSK3β activation inhibits IRE1α-dependent XBP-1 splicing. PERK branch can induce NF-κB activation essentially by translation attenuation of the free IκBα mediated by phosphorylated eIF2α. Additionally, PERK-eIF2α could also contributes to inflammation via ATF4 or PI3K-Akt pathway. Both of NOD1 and Nrf2 could be activated by PERK and IRE1, but Nrf2 has both positive and negative effects on NF-κB, dependent on cellular circumstances. Through the ATF6 branch transient phosphorylation of Akt activates NF-κB, whereas ATF6 activation could inhibit Akt-GSK3β and enhance NF-κB signaling. Additionally, ER E3 ubiquitin ligase, TRIM13 ubiquitylates NEMO and prevents nuclear translocation of NF-κB. CHOP could be activated by all three branches of UPR, causing ROS-mediated ER stress and NF-κB inhibition or activation. ER stress-induced NLRP3 inflammasome is dependent on NF-κB and UPR activation. Signal 1 of NLRP3 inflammasome activation is transcriptional upregulation of NLRP3 along with pro-IL-1β provided by NF-κB. Signal 2 is a posttranscriptional modification which can be provided by ROS. NF-κB controls the levels of ROS by regulating anti-oxidant and pro-oxidant genes, and ROS in turn inhibits or enhances the DNA binding activity of NF-κB itself, depending on modifications of NF-κB. ROS also regulates the IKK complex and phosphorylates IκBα. ROS produced by Nox4 transduces ER stress signals to the UPR to maintain homeostasis, whereas ROS produced by ERO1 or mitochondrial damage leads to cell death. ROS, NF-κB, NLRP3 inflammasome and the production of IL-1β and IL-18, in turn, trigger chronic ER stress.