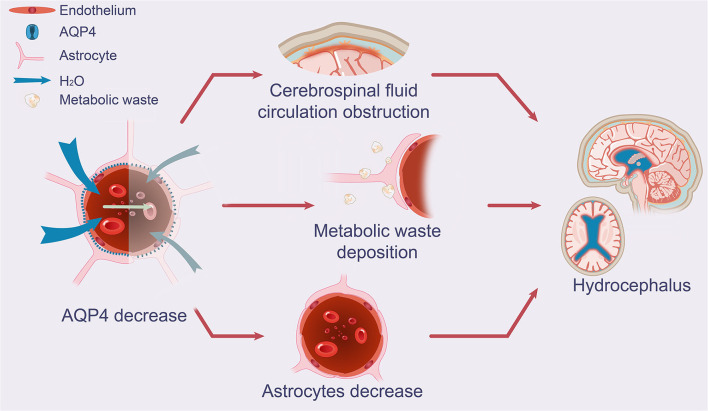
Figure 2.
Effect of AQP4 on potential glymphatic dysfunction and growth of astrocytes in iNPH. The schematic drawing demonstrates decreases in AQP4 and its function in iNPH, which leads to diminished CSF periarterial inflow, CSF-ISF exchange, and perivenous outflow of CSF mediated by AQP4 depolarization, as seen in patients with iNPH. Increased concentrations of neuronal metabolic waste products in the brain interstitial space result from the decreased exchange of CSF and ISF. A decrease in AQP4 in the end-feet of astrocytes near arteries was substantially associated with astrocyte growth and CSF circulation obstruction. AQP4, aquaporin 4; iNPH, idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ISF, interstitial fluid.