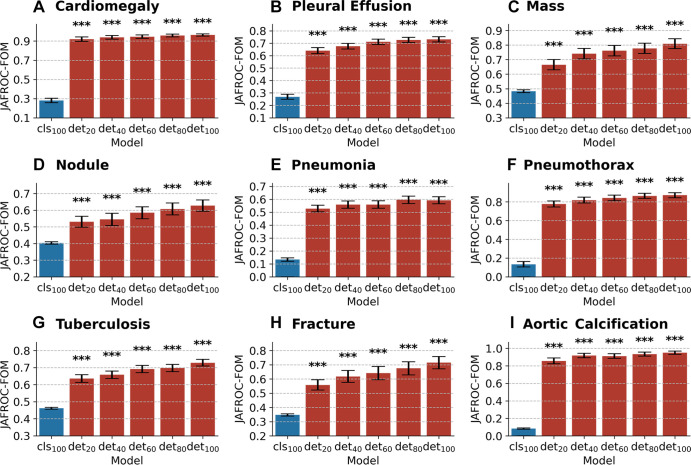
Figure 6:
Bar plots with error bars show comparison of lesion detection performance among models on the internal testing set. CheXNet developed with 100% data (cls100) is compared against CheXDet developed with different ratios of data (det20, det40, det60, det80, and det100; subscripts denote ratios of training data). Blue bars represent jackknife alternative free-response receiver operating characteristic (JAFROC) figures of merit (FOMs) with 95% CIs of CheXNet, and red bars represent JAFROC FOMs with 95% CIs of CheXDet. Whiskers represent the 95% CIs. CheXDet performs higher than CheXNet on the internal lesion detection task, even when trained with 20% of the data. *** represents P < .001.