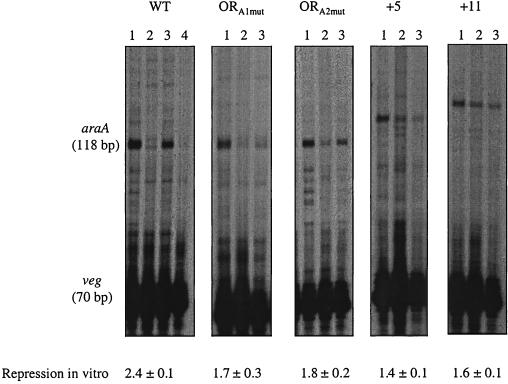
FIG. 5.
In vitro transcription of araABDLMNPQ-abfA operon wild-type versus mutant promoters. Linear plasmid DNA (2 to 4 nM) carrying the araABDLMNPQ-abfA wild-type (WT) or the ORA1mut, ORA2mut, +5, and +11 mutant promoters and the veg promoter were the templates in the experiments. All reactions were carried out in the presence of 1.2 μg of purified His-tag B. subtilis RNA polymerase as described in Materials and Methods. Lanes 1, no AraR added; lanes 2, 25 nM AraR, lanes 3, 25 nM AraR plus 15 mM l-arabinose; lane 4, for the WT promoter only, 25 nM AraR plus 15 mM d-xylose. The AraR-His6 concentration was calculated considering a pure dimeric protein. The positions of the runoff transcripts of the expected sizes are indicated, as judged by the migration of DNA sequencing reactions. To calculate repression in vitro by AraR, the amount of transcript detected by densitometric analysis in the absence of l-arabinose is divided by the amount of transcript detected in the presence of l-arabinose, both standardized with the veg signal in the same lane. The values of repression in vitro are the average ± the standard deviation of two independent experiments except for the wild-type promoter value, which is the result of four independent experiments.