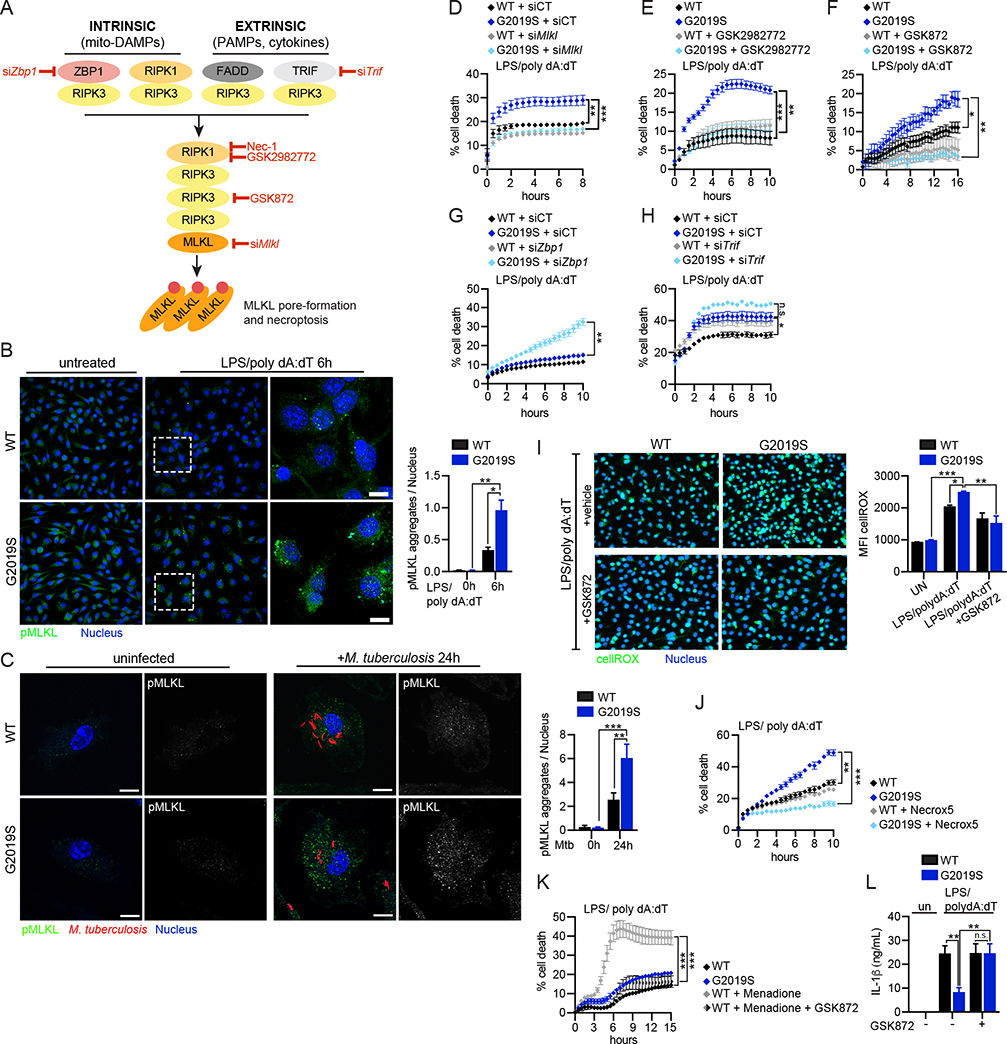
Figure 6. GSDMD-dependent alteration of mitochondrial homeostasis triggers RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL-dependent necroptotic cell death in Lrrk2G2019S BMDMs.
A. Cell-intrinsic and cell-extrinsic signaling cascades that trigger necroptosis. Red = steps in the pathway tested for involvement in Lrrk2G2019S cell death B. Phospho-MLKL aggregation at 6h post-AIM2 stimulation in WT and Lrrk2G2019S BMDMs. (right) pMLKL aggregates/nuclei quantified using Fiji. C. As in B but at 24h post-Mtb infection (MOI 2) D. % cell death following AIM2 activation in WT and Lrrk2G2019S BMDMs transfected with an siRNA against Mlkl (siMlkl) or a non-targeting control siRNA (siCT) E. As in D, but +/− the RIPK1 inhibitor GSK2982772 (10 μM) F. As in D, but +/− RIPK3 inhibitor GSK872 (1 μM) G. As in D, but after transfection with siZbp1 H. As in G but with siTrif I. CellRox (green) and NucBlue (blue) staining in WT and Lrrk2G2019S BMDMs 2h post-AIM2 activation +/− RIPK3 inhibitor GSK872 (1 μM) or DMSO (vehicle). MFI on right. J. % cell death following AIM2 activation in WT and Lrrk2G2019S BMDMs +/− the mitochondrial ROS scavenger Necrox-5 (25 μM) K. % cell death following menadione treatment (25 μM) in WT BMDMs after AIM2 activation +/− GSK872 (1 μM) L. Extracellular IL-1β protein levels as measured by ELISA at 6 h post AIM2 stimulation in WT and Lrrk2G2019S BMDMs +/− RIPK3 inhibitor GSK872 (1 μM) Statistical analysis: n=3 or more unless otherwise noted. Statistical significance determined using a two-tailed Student’s T test (B, C), a two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test (D-H, J, K), or a one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test (I, L).