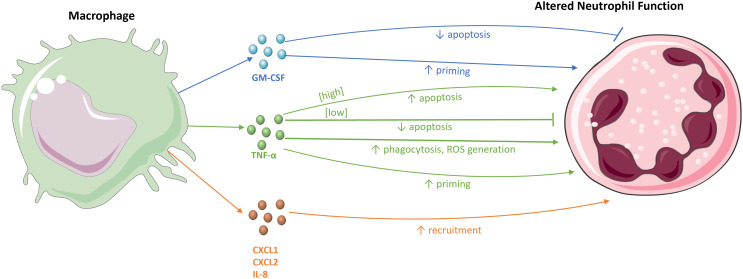
Figure 2.
The effects of macrophages on neutrophils. Macrophages and their chemokines, CXCL1, CXCL2, and IL-8, recruit neutrophils to sites of infection and inflammation. The macrophage-derived cytokines, TNF-α and GM-CSF, modulate neutrophil survival, either by inhibiting or stimulating apoptosis. These cytokines also influence various immune effector functions of neutrophils, for example, by priming the respiratory burst and increasing neutrophil phagocytosis and ROS generation.