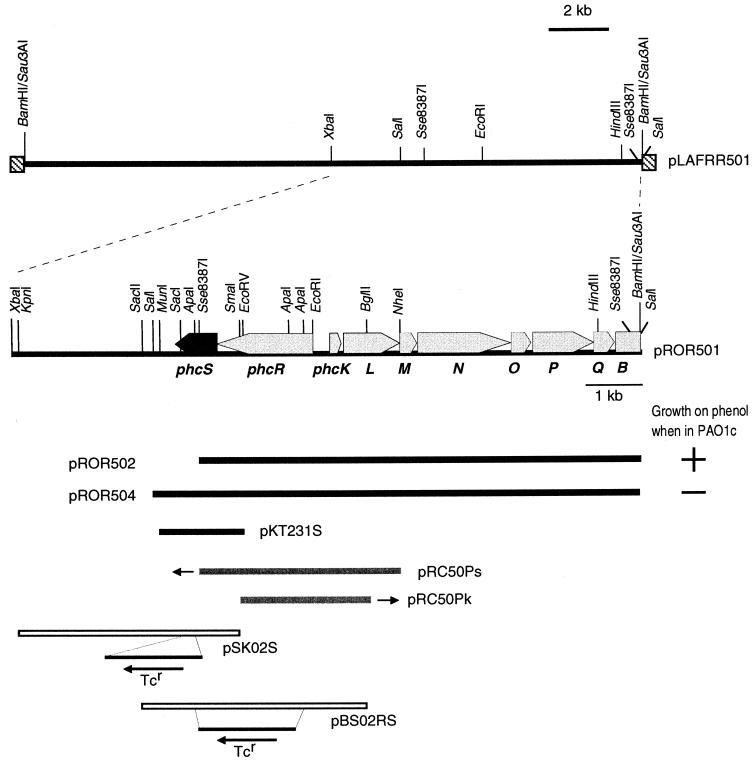
FIG. 1.
Genetic organization of the regulatory and structural genes for mPH in C. testosteroni R5. phcS (in black) was identified in this study. The other genes were identified in our previous study (50). The arrows indicate the direction of transcription. The ability (+) or inability (−) of plasmids pROR502 and pROR504 to allow P. putida PAO1c to grow on phenol as the sole carbon source is indicated. pKT231S is a derivative of pKT231 and carries a MunI-EcoRV fragment which contains the phcS gene, while pRC50Ps is a derivative of pRC50 and carries an Sse8387I-NheI fragment which contains phcR. pRC50Pk is also a derivative of pRC50 and carries an EcoRV-BglII fragment which contains a phcK promoter region. The two small arrows indicate the direction of lacZ on plasmids pRC50Ps and pRC50Pk. pSK02S carries the phcS gene which was disrupted by the insertion of a tetracycline resistance gene (Tcr) cassette, while pBS02RS carries the phcS and phcR genes which were disrupted by the insertion of a Tcr cassette.