Fig. 2 |. Association of baseline circulating NBL1 with risk of ESKD in the study cohorts during 10-year follow-up.
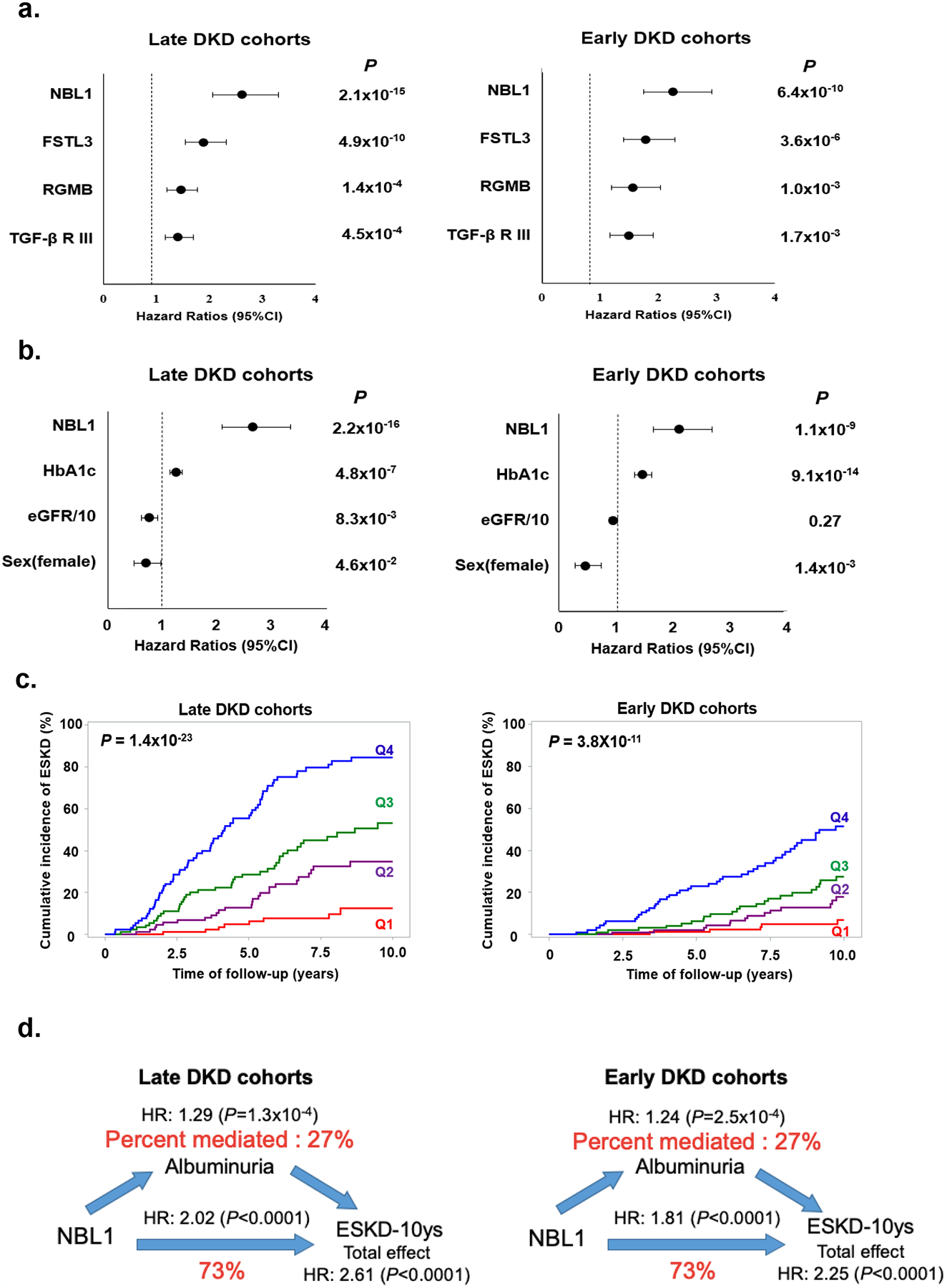
a. Risk of ESKD according to baseline circulating concentration of each of 4 confirmed proteins in late and early DKD cohorts. Results of Cox regression analysis are shown. Effect measures were expressed as HR and 95% CI per standard deviation (SD) increase in protein concentration. Effect for each protein was adjusted for sex, duration of diabetes, HbA1c, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and baseline eGFR with stratification of type of diabetes.
b. Effect of baseline circulating concentration of NBL1 on risk of ESKD after adjustment for other candidate proteins and baseline clinical characteristics. Results of Cox regression analysis with backward elimination of covariates are shown. Factors considered were NBL1, FSLT3, RGMB, TGF-βRIII, sex, duration of diabetes, HbA1c, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and baseline eGFR. Results are shown for late and early DKD cohorts. Effect measures were expressed as HR and 95% CI per SD increase in NBL1 concentration, 1% increase in HbA1c, 10 ml change in baseline eGFR, and 1 for women and 0 for men. P<0.05 was used to retain variables.
c. Cumulative incidence of ESKD according to quartiles of baseline circulating concentration of NBL1 in late and early DKD cohorts. Q1, First quartile; Q2, Second quartile; Q3, Third quartile; Q4, Fourth quartile.
d. Mediation analysis of association between baseline circulating concentrations of NBL1 and risk of ESKD during 10-year follow-up according to baseline albuminuria (ACR) in late and early DKD cohorts. NBL1 concentration was considered as exposure, risk of ESKD was outcome and ACR was mediator. In the analyses we used Cox regression model for 10-year risk of ESKD adjusted for sex, duration of diabetes, HbA1c, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and baseline eGFR with stratification of type of diabetes. Effect measures were expressed as the HR per SD increase in NBL1 concentration. The effect of a NBL1 on ESKD (total effect) is split into a natural indirect effect (through ACR) and natural direct effect, which is independent from the ACR.
