Figure 4.
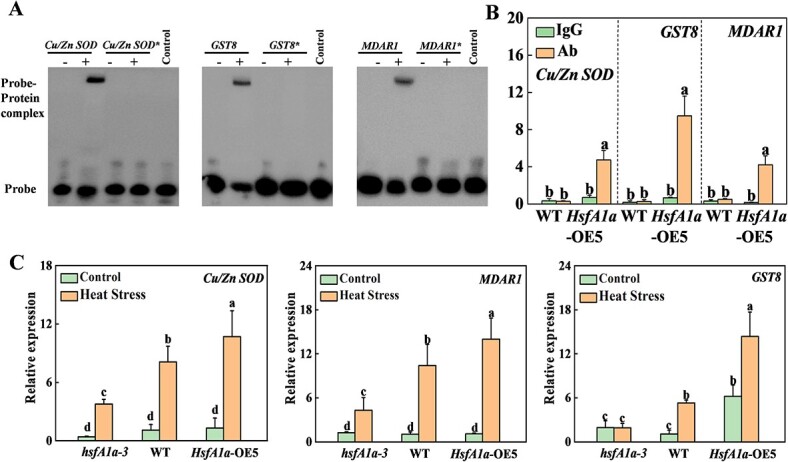
HsfA1a transcriptionally regulates Cu/Zn SOD, GST8, and MDAR1 genes in anthers under heat stress. (A) EMSA showing binding of HsfA1a to HSE sequences of the promoters of Cu/Zn SOD, GST8, and MDAR1. Recombinant HsfA1a was used in DNA binding assays to Cu/Zn SOD, GST8, MDAR1, and their HSE motif sequences as probes. His was used as the negative control. The asterisk (*) represents a mutated probe. All probes are listed in Supplementary Data Table S4. (B) Binding of HsfA1a to the Cu/Zn SOD, GST8, and MDAR1 promoters in 35S-HsfA1a-HA-overexpressing (HsfA1a-OE) plants was analyzed using ChIP–qPCR. WT and HsfA1a-OE plants at flowering stage were subjected to heat-stress treatment, anther samples were taken, and input chromatin was isolated from them. Anti-HA antibody was applied for immunoprecipitation of HsfA1a–chromatin complexes. Control reactions used mouse IgG. qRT–PCR was used to quantify input and ChIP DNA samples with specific primers for the promoters of Cu/Zn SOD, GST8, and MDAR1 genes. The percentages of input DNA are displayed as ChIP results. (C) Relative expression of Cu/Zn SOD, GST8, and MDAR1 genes in anthers of hsfA1a, WT, and HsfA1a-OE plants under control or heat stress. Means with the same letter in Tukey’s test indicate a non-significant difference at P < .05. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. hsfA1a-3, one line of hsfA1a mutants; HsfA1a-OE5, one line of HsfA1a OE plants.
