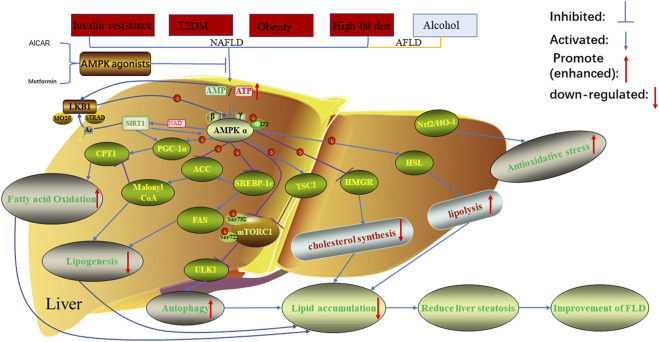
FIGURE 1.
Regulation of AMPK on lipid metabolism in FLD. In the case of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease caused by insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, obesity, high-fat diet and alcoholic fatty liver disease caused by alcohol, the related proteins in AMPK signaling pathway will be inhibited or promoted, resulting in increased lipid accumulation and decreased fatty acid oxidation. This was reversed when AMPK was treated with AMPK agonists. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; AICAR, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide; LKB1, Liver kinase B1; the auxiliary subunit STRAD, STE20 related adaptor protein, and MO25, Mouse protein 25; Sirt1, Silent mating type information regulation two homolog1; CPT1, carnitine acyltransferase one; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ co-activator -1α; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; SREBP-1c, Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c; FAS, fatty acid synthase; TSC2; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin1; ULK1, unc51 like kinase one; HMGR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; HSL, Hormone-Sensitive triglyceride lipase; Nrf2/HO-1, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1.