Fig. 1.
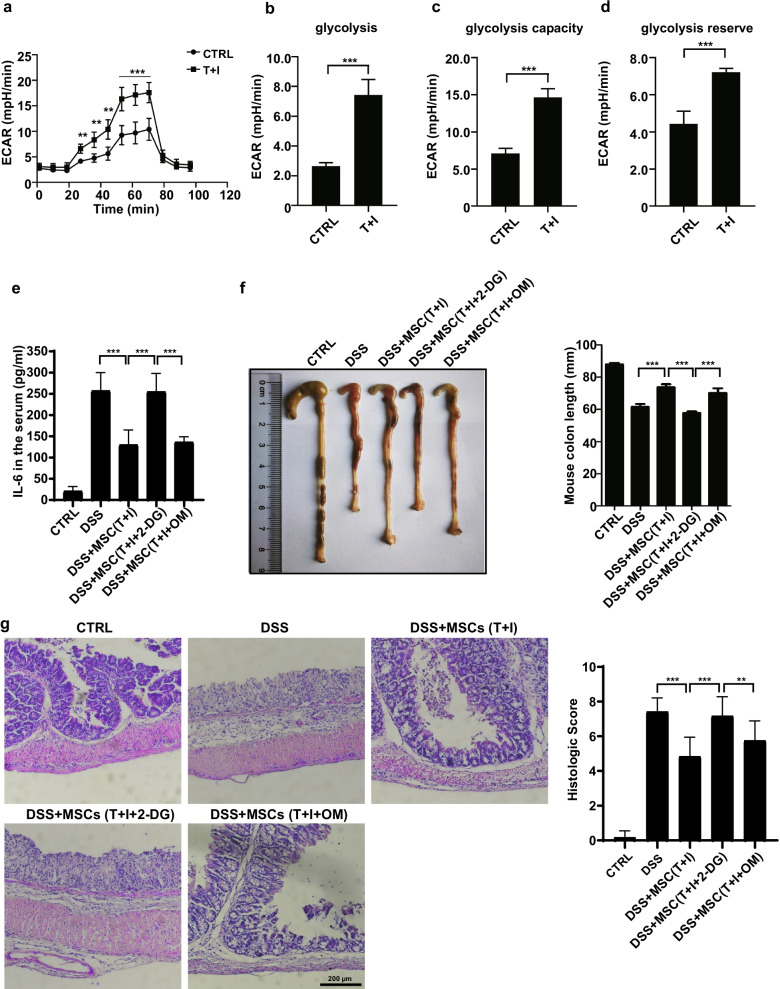
TNFα- and IFNγ-induced glycolysis is required for the therapeutic effect of hUC-MSCs on IBD. a Extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) of hUC-MSCs treated with or without TNFα and IFNγ for 24 h (TNFα and IFNγ, 10 ng/ml each; n = 4 for each group; repeated three times). ECAR was measured under basal conditions, in response to 10 mM glucose (= basal glycolysis), and upon blocking the mitochondrial ATP generation by 1 µM oligomycin. Compensatory effects on ECAR following interference with oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) represent the maximal glycolysis capacity. b The basal and c maximal glycolysis values in figure (a) were statistically analyzed. d Calculation of the glycolysis reserve is subtraction basal glycolysis from maximal glycolysis. e The IL-6 protein levels in the serum were examined by ELISA. f The colon length of IBD mice treated with hUC-MSCs. The right panel shows the statistic of the colon length of IBD mice. g The representative H&E stained colon sections of IBD mice treated with the hUC-MSCs and their histological scores. Scale bar, 200 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ***, p < 0.001. n = 5 for each groups