Fig. 2.
Contribution of Genetic Aberrations in Wnt Pathways in Gastrointestinal Cancers
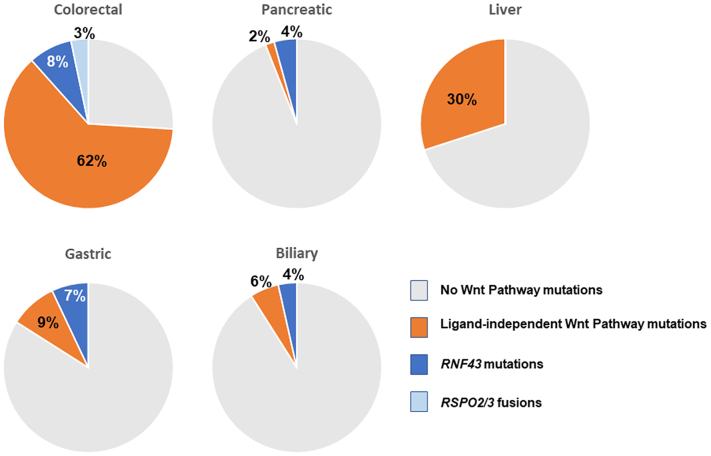
Mutations or fusions in Wnt pathway genes are common in gastrointestinal cancers. Of these, the majority occur in downstream components such as CTNNB1 and APC, which are expected to be largely independent of extracellular Wnt ligands, although ligand-dependent aberrations such as RNF43 mutations or RSPO2/3 fusions are also observed. Mutation data from cBio Portal, (Cerami et al., 2012; Gao et al., 2013), using curated non-overlapping datasets, n = 1564 samples for CRC, n = 922 for pancreatic cancer, n = 1111 for liver cancer, n = 795 for gastric cancer, n = 588 for biliary cancer. CBio Portal accessed 27th Oct 2021. Since RSPO2/3 fusions are not captured in cBio, prevalence is per literature reports (Kleeman et al., 2020).