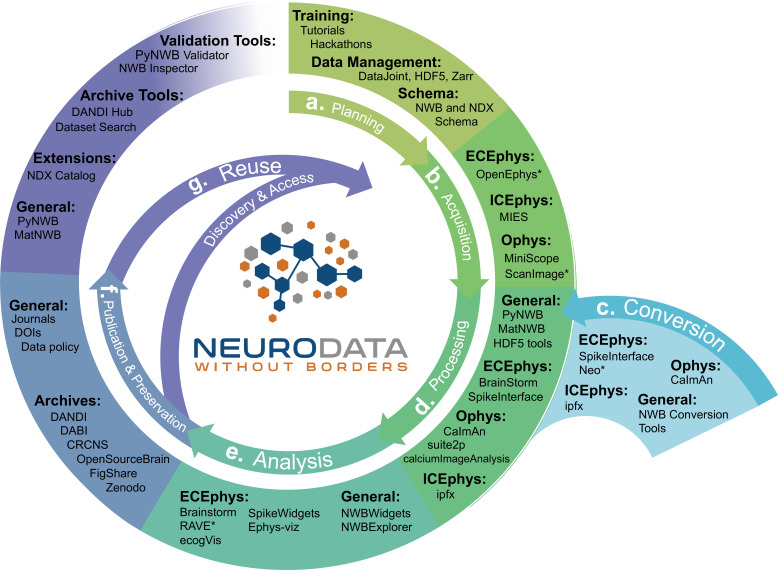
Figure 6. NWB is integrated with state-of-the-art analysis tools throughout the data life cycle.
NWB technologies are at the heart of the neurodata lifecycle and applications. Data standards are a critical conduit that facilitate the flow of data throughout the data lifecycle and integration of data and software across all phases (a. to g.) of the data lifecycle. (a) NWB supports experimental planning through integration with data management, best practices, and by allowing users to clearly define what metadata to collect. (b–c) NWB supports storage of unprocessed acquired electrical and optical physiology signals, facilitating integration already during data acquisition. NWB is already supported by several acquisition systems (b) as well as a growing set of tools for conversion (c) of existing data to NWB. (d) Despite its young age, NWB is already supported by a large set of neurophysiology processing software and tools. Being able to access and evaluate multiple processing methods, e.g., different spike sorting algorithms and ROI segmentation methods, is important to enable high-quality data analysis. Through integration with multiple different tools, NWB provides access to broad range of spike sorters, including, MountainSort, KiloSort, WaveClust, and others, and ophys segmentation methods, e.g., CELLMax, CNMF, CNMF-E, and EXTRACT. (e) For scientific analysis, numerous general tools for exploration and visualization of NWB files (e.g. NWBWidgets and NWBExplorer) as well as application-specific tools for advanced analytics (e.g. Brainstorm) are accessible to the NWB community. (f–g) NWB is supported by a growing set of data archives (e.g. DANDI) for publication and preservation of research data. Data archives in conjunction with NWB APIs, validation tools, and the NDX Catalog play a central role in facilitating data reuse and discovery.