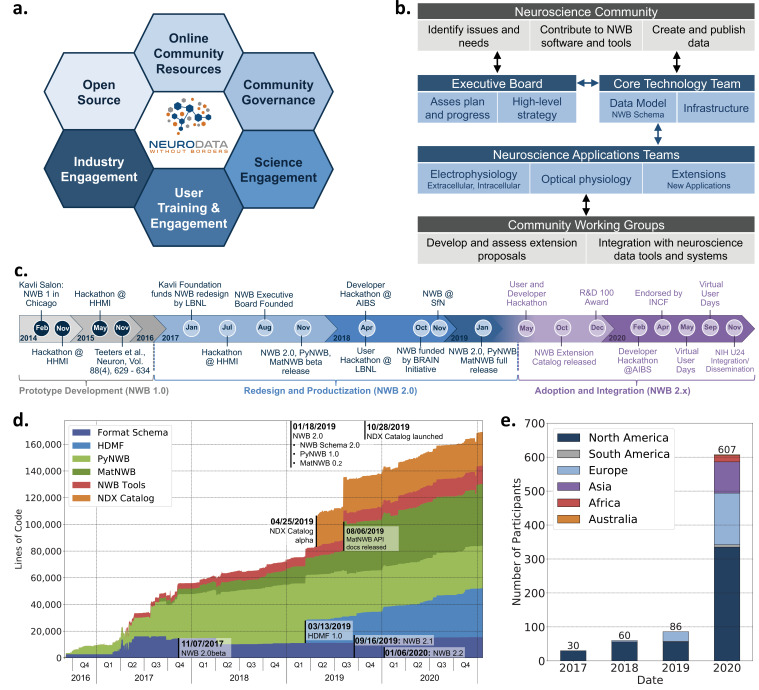
Figure 8. Coordinated community engagement, governance, and development of NWB.
(a) NWB is open source with all software and documents available online via GitHub and the nwb.org website. NWB provides a broad range of online community resources, e.g., Slack, online Help Desk, GitHub, mailing list, or Twitter, to facilitate interaction with the community and provides a broad set of online documentation and tutorials. NWB uses an open governance model that is transparent to the community. Broad engagements with industry partners (e.g. DataJoint, Kitware, MathWorks, MBFBioscience, Vidrio, CatalystNeuro, etc.) and targeted science engagements with neuroscience labs and tool developers help sustain and grow the NWB ecosystem. Broad user training and engagement activities, e.g., via hackathons, virtual training, tutorials at conferences, or online training resources, aim at facilitating adoption and growing the NWB community knowledge base. (b) Organizational structure of NWB showing the main bodies of the NWB team (blue boxes) and the community (gray boxes), their roles (light blue/gray boxes), and typical interactions (arrows). (c) The timeline of the NWB project to date can be roughly divided into three main phases. The initial NWB pilot project (2014–2015) resulted in the creation of the first NWB 1.0 prototype data standard. The NWB 2.0 effort then focused on facilitating use and long-term sustainability by redesigning and productizing the data standard and developing a sustainable software strategy and governance structure for NWB (2017–2019). The release of NWB 2.0 in Jan. 2019 marked the beginning of the third main phase of the project, focused on adoption and integration of NWB with neuroscience tools and labs, maintenance, and continued evolution and refinement of the data standard. (d) Overview of the growth of core NWB 2.x software in lines of code over time. (e) Number of participants at NWB outreach and training events over time. In the count we considered only the NWB hackathons and User Days (see c.), the 2019 and 2020 NWB tutorial at Cosyne, and 2019 training at the OpenSourceBrain workshop (i.e. not including attendees at presentations at conferences, e.g., SfN).