Figure 1.
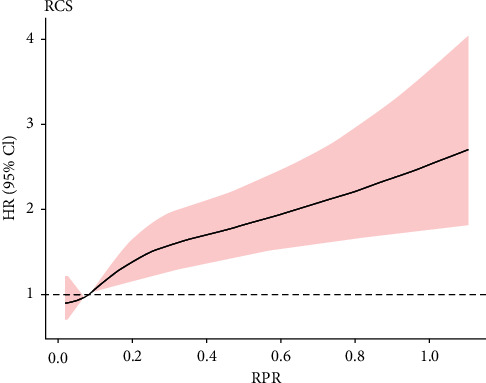
The relationship between RPR levels and 28-d mortality in patients with sepsis was plotted using multivariable adjusted restricted cubic splines. There was a nonlinear relationship between RPR and 28-d mortality, showing a trend of rapid first and then gradually increasing, that is, the higher the RPR level, the higher the mortality risk. The range area represents a 95% confidence interval. HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; RPR: red cell distribution width to platelet ratio.
