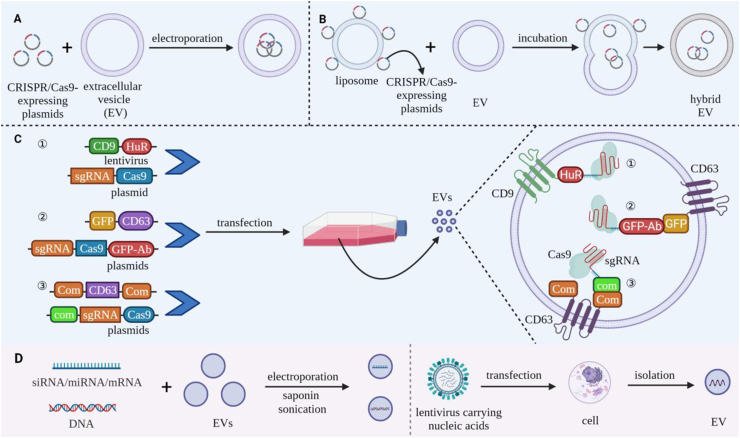
Figure 6.
Strategies for loading bioactive components into EVs for gene therapy. (A‒C) Load approaches for CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing systems. (A) Electroporation-mediate loading of Cas9/sgRNA-expressing plasmids into large-diameter EVs. (B) EV fusion with liposomes that are surface loaded with Cas9/sgRNA-expressing by electrostatic interaction, which transfers these plasmids to the lumen of the resulting hybrid EVs. (C) Transfection of parental cells with vectors that express fusion proteins that induce the EV enrichment of recombinant Cas9/sgRNA complexes. Approaches reported to date include: ① CD9-HuR fusion protein-mediated capture of CRISPR/Cas9 complexes containing an miR-155-tagged sgRNA. ② CD63-GFP fusion-protein mediated capture of CRISPR/Cas9 complexes containing a Cas9-GFP nanobody fusion protein. ③ CD63-com fusion protein capture of CRISPR/Cas9 complexes that contain sgRNA modified with the com aptamer (D) EV loading with nucleic acids (e.g., siRNA, miRNA, mRNA, and DNA). By electroporation, sonication, or saponin-mediated membrane permeation, or during EV biogenesis in parental cells following lentivirus transfection.