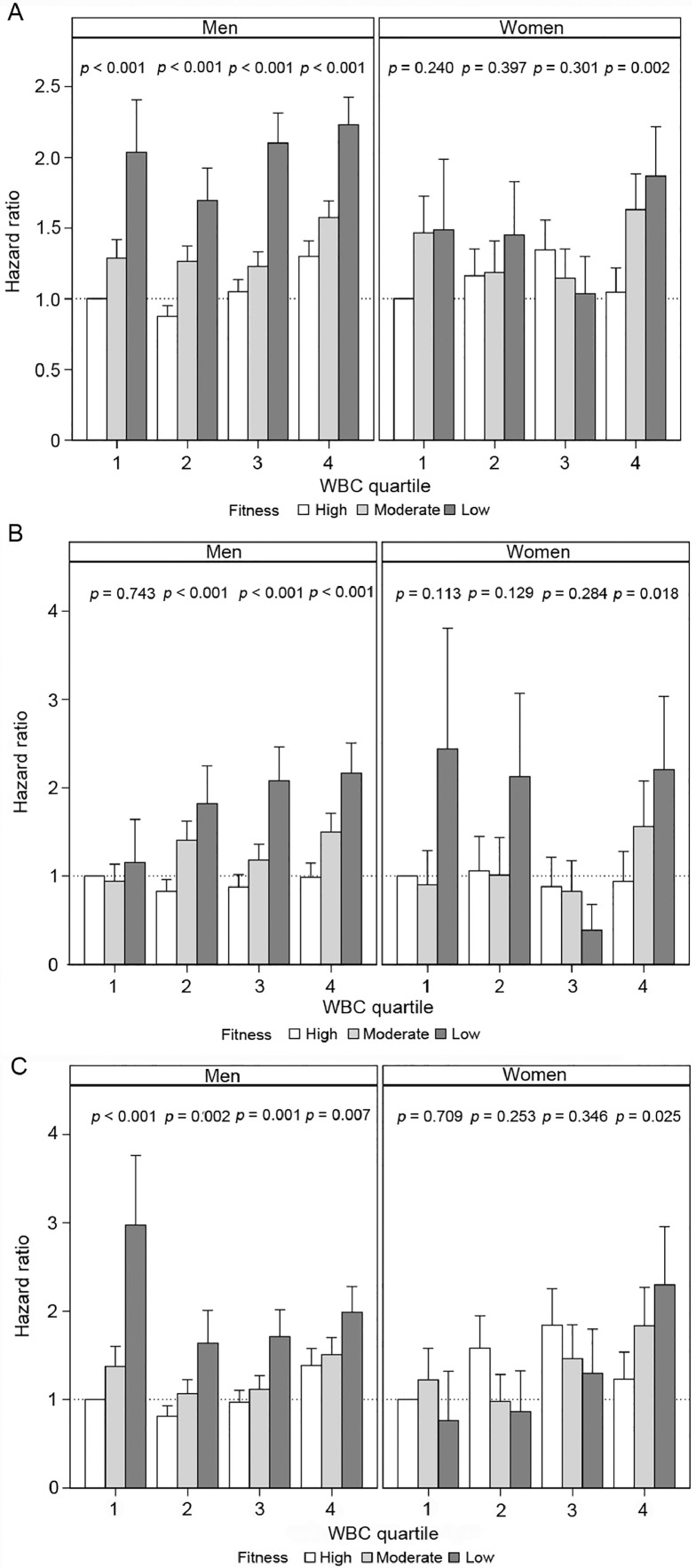
Fig. 1.
(A) All-cause mortality; (B) cardiovascular disease; and (C) cancer mortality hazard ratios relative to low fit. White blood cell count (WBC) Quartile 1, in men and women with standard error bars, referent value (dotted), and inset fitness trend tests within WBC quartiles. Interaction p values were (A) 0.42 (men) and 0.48 (women); (B) 0.57 (men) and 0.61 (women); and (C) 0.54 (men) and 0.38 (women), supporting the hypothesis that the relationship of fitness and all-cause mortality is independent of WBC (the Cooper Center Longitudinal Study (CCLS), 1978–2016).