FIG. 1.
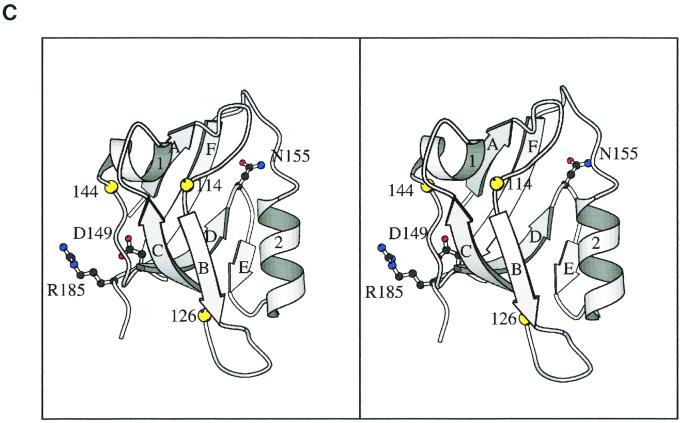
The SpoIVB PDZ domain. (A) Schematic diagram showing the position of the PDZ domain of SpoIVB (residues 102 to 187). The arrow indicates the site of the first self-cleavage reaction in the SpoIVB polypeptide. Also shown are the propeptide sequence, the region containing the serine peptidase domain, and a region thought to be involved in SpoIVB's putative second function (shaded box). (B) Structure-based sequence alignment of the putative PDZ domain in B. subtilis SpoIVB (accession no. P17896; residues 102 to 187; Sp4B, center) with four PDZ domains of known structure (above the Sp4B sequence) and four SpoIVB homologues (below the Sp4B sequence). Amino acid identity and similarity between the groups are indicated (h, hydrophobic; s, small; −, negative charge; +, positive charge). A consensus secondary structure (α1 and α2, α helices; βA to -F, β strands) is given above the PDZ sequences. Note that all gaps and insertions required for maximal primary sequence alignment are placed outside of these structural elements. Residues known to contact ligands based on the structures of PDZ-peptide complexes are underlined. The positions of mutations in B. subtilis SpoIVB are indicated by arrows. These correspond to three positions that are conserved between the two groups (G114, D149, and N155) and three which are conserved within the SpoIVB group (G126, G144, and R185). Of the 286 PDZ domains identified by the Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool (33), Gly114 is conserved in 266 sequences, Gly126 is conserved in 114, Gly144 is conserved in 156, Asp149 is conserved in 269, Asn155 is conserved in 209, and Arg185 is conserved in 37. Preliminary sequence data were obtained from The Institute for Genomic Research (www.tigr.org), the B. stearothermophilus Genome Sequencing Project at the University of Oklahoma (www.genome.ou.edu), and Genome Therapeutics Corp. (www.cric.com). Pdz1, brain postsynaptic density protein 95 (residues 312 to 397); Pdz2, rabbit α-syntrophin (residues 80 to 164); Pdz3, neuronal nitric oxide synthase (residues 15 to 101); Pdz4, hCASK (residues 482 to 574). Bant, B. anthracis; Bste, B. stearothermophilus; Bhal, B. halodurans (BAB06494); Cace, Clostridium acetobutylicum. (C) Stereoscopic representation of the SpoIVB PDZ domain structure. A homology model of the B. subtilis SpoIVB PDZ domain was constructed based on the crystal structures of PDZ 1 to 4 (Protein Data Bank codes 1be9, 1qav, 1qau, and 1kwa; [7, 8, 14]) by using the program Modeller (29). The peptide-binding groove is between βB and α2, and the carboxylate-binding loop is between βA and βB. The positions of glycine residues 114, 144, and 126 are shown as yellow balls. The side chains of residues Asp149, Asn155, and Arg185 are drawn as ball-and-stick images and colored with carbon atoms in grey, nitrogen atoms in blue, and oxygen atoms in red. The image was drawn with Molscript (16).