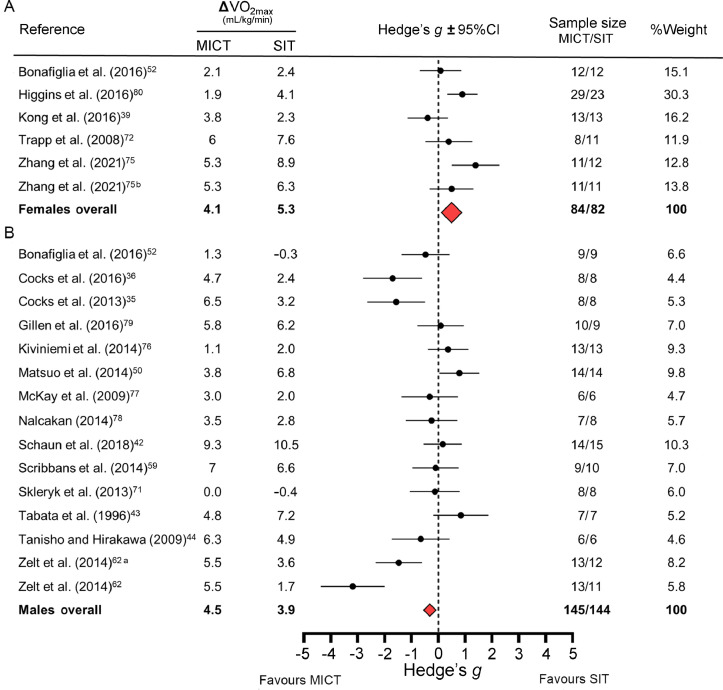
Fig. 3.
Forest plot on subset of studies that reported sex-specific data or included only female or male participants. Forest plot depicts meta-analysis comparing changes in relative maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) following sprint interval training (SIT) and moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) separated by sex: (A) females and (B) males. Because effect sizes were calculated as (SIT minus MICT) divided by pooled standard deviation, negative values reflect larger changes in VO2max following MICT whereas positive values reflect larger changes following SIT. The red diamonds represent the overall weighted effect size (Hedge's g) for each baseline fitness group, and the horizontal points of the diamonds represent the upper and lower bounds of the 95% confidence intervals (95%CIs). Overall changes in VO2max presented as averages, and overall number of participants presented as total sums. Comparison of 1/2 SIT (a) or “all-out” SIT (b) vs. MICT (see Table 1 for details).