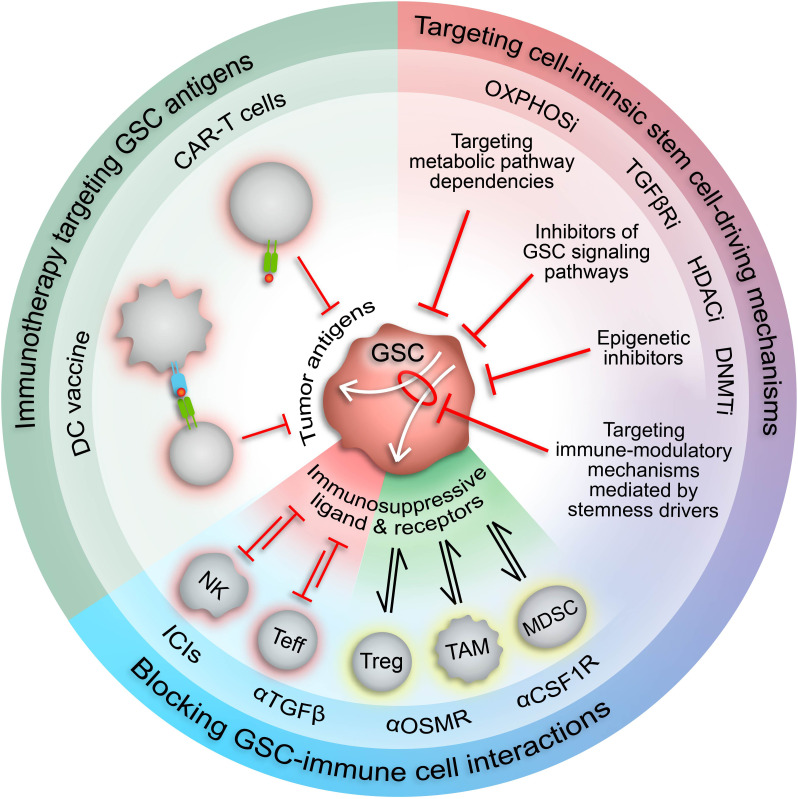
Figure 3.
Therapeutic approaches to target immunosuppressive GSCs. Increased understanding of the malignant properties of GSCs and their inherent plasticity and heterogeneity has designated GSCs as desirable therapeutic targets. The role of GSCs in driving and maintaining an immunosuppressive TME suggests that GSC-targeted therapies could potentiate current immunotherapies. Targeting stemness mechanisms that also mediate immunosuppressive mechanisms in GSCs (white arrows) has the potential to augment immunotherapy response in GBM by increasing expression of tumor-specific antigens and repressing immunosuppressive cell interactions. CAR-T cell, chimeric antigen receptor T cell; DC, dendritic cell; NK, natural killer cell; Teff, effector T cell; Treg, regulatory T cell; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage/microglia; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; ICIs, immune checkpoint inhibitors; HDACi, HDAC inhibitors; DNMTi, DNMT inhibitors; TGFβRi, TGFβ receptor inhibitors; OXPHOSi, oxidative phosphorylation inhibitors.