Fig. 4. Transmission model and reconstruction of the SARS-CoV-2 reporting process in Italy.
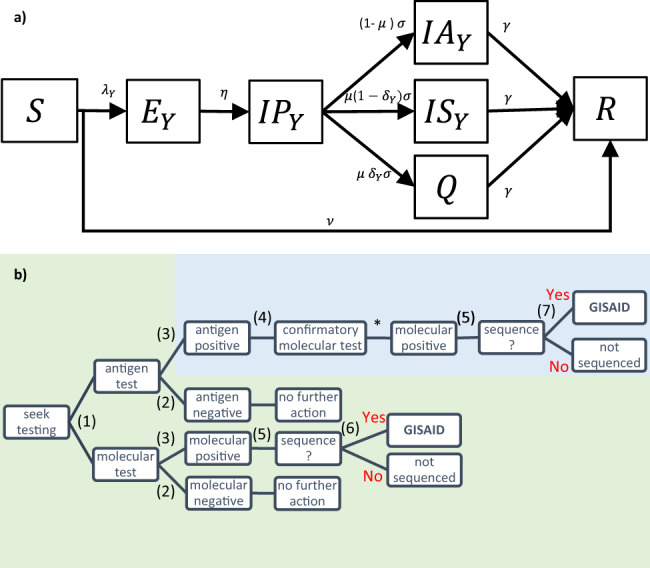
a Simplified flow diagram of the compartmental model used to reproduce the dynamics of the discordant variant M234I-A376T and the concordant variants A220V, Alpha, and other variants, in Veneto and the rest of Italy. Susceptible individuals (S compartment) are infected at rate , where subscript Y refers to the virus variants (M234I-A376T, A220V, Alpha, other variants). Upon infection, the latency period (EY compartment) lasts for an average of days after which individuals are infectious but asymptomatic (IPY compartment) for an average of days. We assume that a proportion () of infections remain asymptomatic (IAY compartment) whilst the remaining proportion (μ) develop symptoms; of these symptomatic individuals we assume that a proportion () are not detected by surveillance (ISY compartment) and the remaining proportion is detected, reported and isolates (Q compartment). After an average infectious period of days individuals recover and test negative (R compartment). Susceptible individuals are vaccinated and enter the R compartment at rate ν. b Description of the Italy testing policy, reproduced in the compartmental model. (1) Symptomatic individuals present for diagnosis with either an antigen or molecular test. (2) Negative test results warrant no further action and individuals contribute to transmission (IS compartment). (3) Individuals with a positive antigen or molecular test result isolate until their recovery (Q compartment, 100% compliance). (4) Positive antigen tests are additionally confirmed with a molecular test. (5) A random proportion of molecular-positive samples are selected for genomic surveillance and reported in GISAID. (6) In the green pathway, both discordant and concordant variant samples will be reported in GISAID. (7) In the blue pathway, only concordant variant samples will return a positive antigen result and be reported in GISAID. As positive antigen cases are confirmed by molecular tests, the probability of reporting a concordant variant in GISAID is independent of the test administered. For the discordant variant, the probability of reporting in GISAID depends on the probability that the initial test is molecular. *Antigen-positive samples are assumed to also be molecular-positive.
