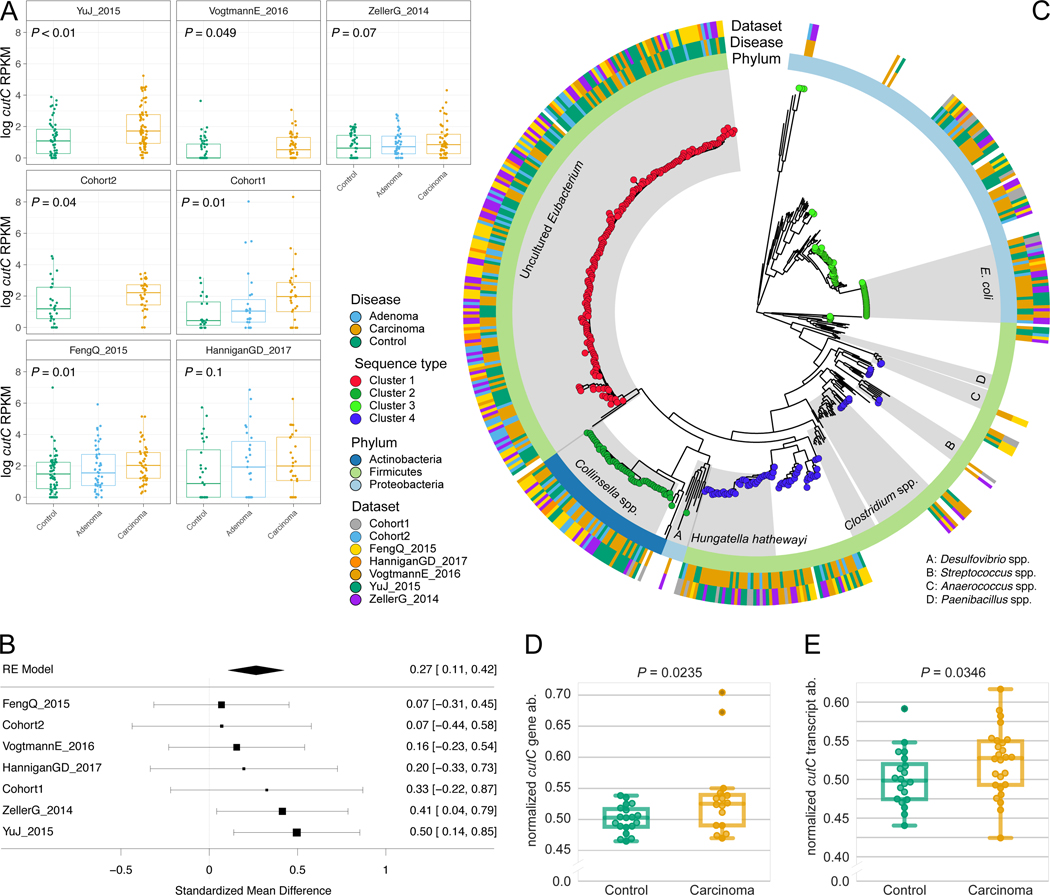
Figure 4. Choline TMA-lyase gene cutC and its genetic variants are strong biomarkers for CRC-associated stool samples.
(A) Distribution of reads per kilobase million (RKPM) abundances obtained using ShortBRED for the choline TMA-lyase enzyme gene cutC. P-values were computed by two-tailed Wilcoxon Signed-Rank tests comparing values between controls and carcinomas for each dataset. (B) Forest plot reporting effect sizes calculated using a meta-analysis of standardized mean differences and a random effects model on cutC RPKM abundances between carcinomas and controls. (C) Phylogenetic tree of sample-specific cutC sequence variants identified four main sequence variants. Tips with no circles represent cutC sequence variants from genomes absent from the datasets. Taxonomy was assigned based on mapping against existing cutC sequences (criteria of 80% coverage, >97% identity and minimum 2,000nt alignment length). (D) qPCR validation of cutC gene abundance and (E) cutC transcript abundance (normalized by total 16S rRNA gene/transcript abundance) on a subset of DNA samples from Cohort1. qPCR validation P-values are obtained by 1-tail Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test.