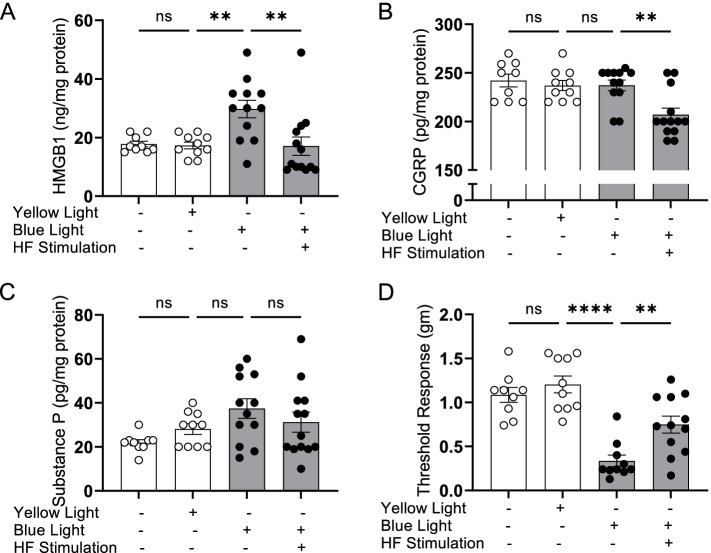
Fig. 3.
HFES reduces optogenetically-induced HMGB1 release and mechanical allodynia. Vglut2-Cre/ChR2-eYFP mice were anesthetized and subjected to optogenetic stimulation using 470 nm LED (blue) or 595 nm LED (yellow light) for 15 min on the dorsum of the right hind paw, followed by transcutaneous HFES of the sciatic nerve for 10 min (5 min perpendicular and parallel to the sciatic nerve, VGlut2-ChR2-YFP mice only (A-C). Levels of HMGB1, CGRP and substance P were measured in paw interstitial fluid at 5 h post-stimulation. Data is represented as individual mouse data points with mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test between groups. N = 5-12 per group. *: P < 0.05. **: P < 0.01. ns: not significant. D Mechanical hypersensitivity was assessed 5 h later using von Frey filaments. HFES significantly improves optogenetically-induced mechanical hypersensitivity as compared to sham stimulated mice. Data is represented as individual mouse data points with mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test between groups. N = 5-12 per group. **P < 0.01. **** P < 0.0001. ns: not significant